Share your love
Install and Use Cockpit on Debian 11

In this article, we want to teach you How To Install and Use Cockpit on Debian 11.
Cockpit is a web-based interface for Linux servers with a friendly interface where you can manage storage, networking, firewall, and containers, to name a few. You can even open a terminal session right on your web browser when you need to break out the command line!
How To Install and Use Cockpit on Debian 11
To install Cockpit, you need to log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide the Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Set up Cockpit on Debian 11
By default, the Cockpit packages are available in the default Debian repository. First, update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt update
Then, use the following command to install Cockpit on your server:
sudo apt install cockpit -y
Next, start your Cockpit service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start cockpit.socket
Enable it to start on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable cockpit.socket
Now verify your Cockpit service is active and running on Debian 11 with the command below:
sudo systemctl status cockpit.socketOutput ● cockpit.socket - Cockpit Web Service Socket Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket; enabled; vendor preset: > Active: active (listening) since Wed 2022-06-08 02:30:45 EDT; 8s ago Triggers: ● cockpit.service Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8) Listen: [::]:9090 (Stream) Process: 13768 ExecStartPost=/usr/share/cockpit/motd/update-motd localhost (> Process: 13775 ExecStartPost=/bin/ln -snf active.motd /run/cockpit/motd (code> Tasks: 0 (limit: 2340) Memory: 8.0K CPU: 15ms CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.socket
At this point, you need to configure the firewall for Cockpit. We assumed that the UFW firewall is installed and configured on your system then you will need to allow ports 80 and 9090 through the UFW firewall. To do this, run the commands below:
# sudo ufw allow 9090 # sudo ufw allow 80
Then, reload the firewall to apply the new rules:
sudo ufw reload
You can check your UFW firewall status with the following command:
sudo ufw status
Output
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
9090 ALLOW Anywhere
80 ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
9090 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)Access Cockpit Web Interface
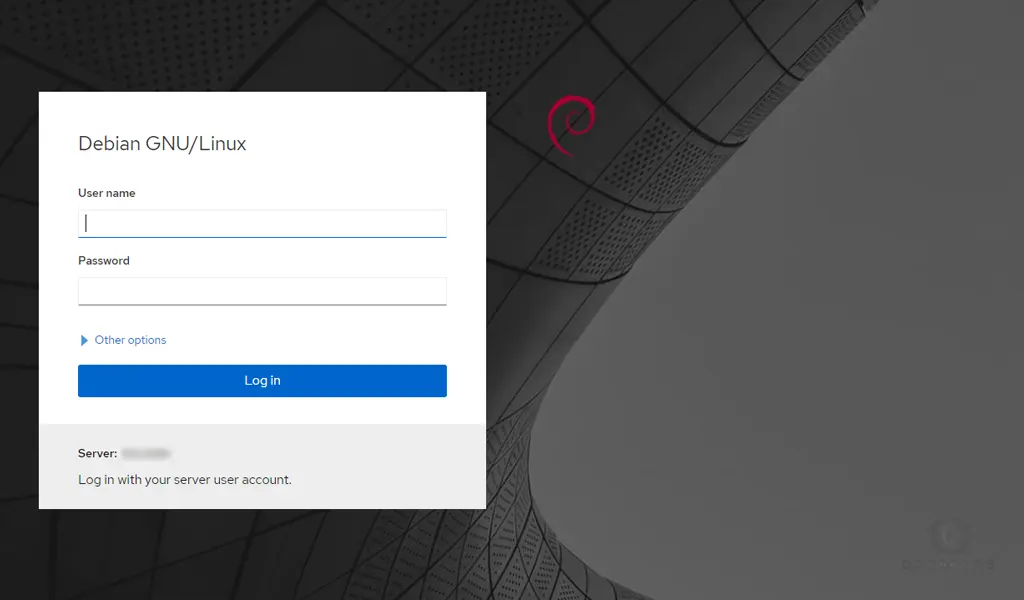
At this point, you can access the Cockpit web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 9090:
http://your-server-ip:9090You should see the Cockpit login screen. Provide your root username, and password and click on Login.
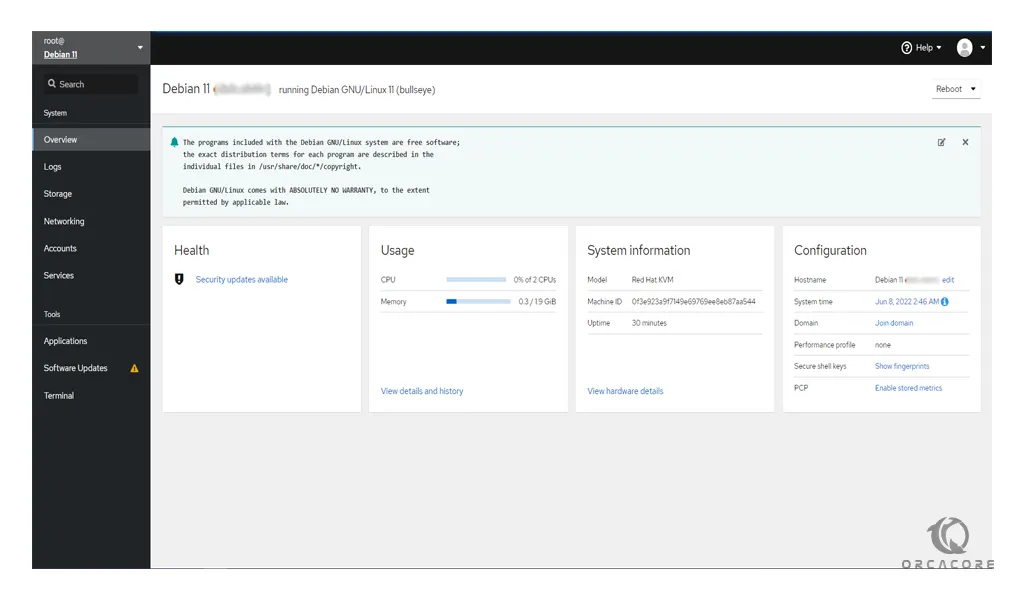
Now you will see your Cockpit dashboard:
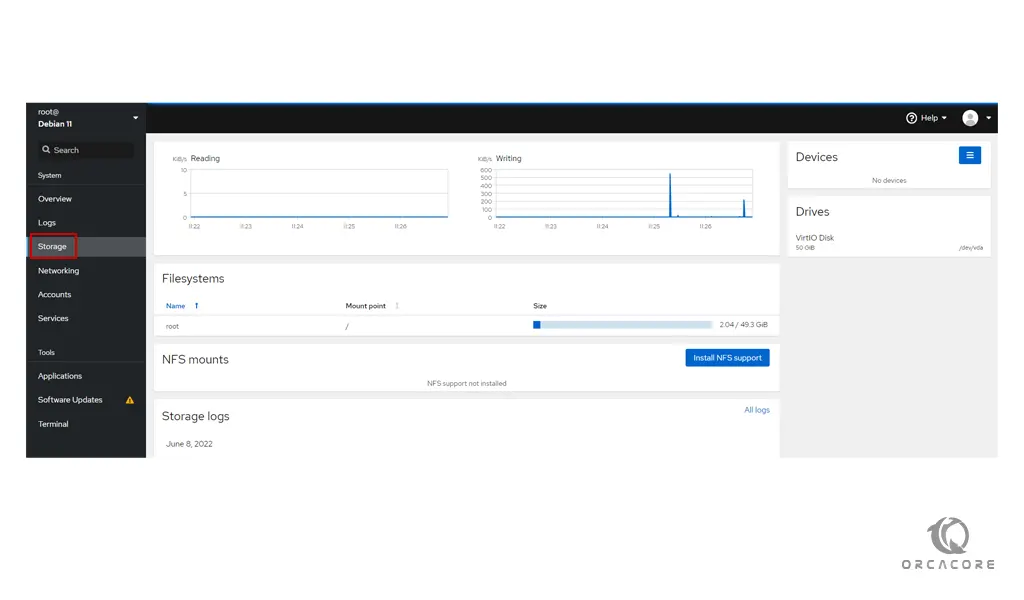
To see your system’s partition information, click on Storage in the left pane:
Also, you can see the network-related information by clicking on the Networking:

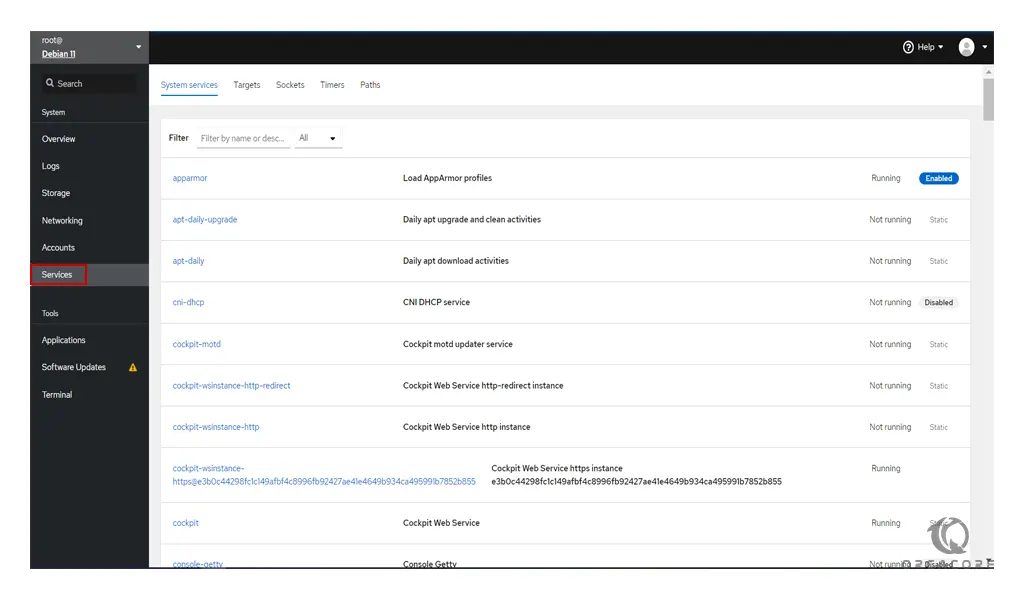
Click on the Services. You should see all system services.
From the Applications, you should see all installed applications.
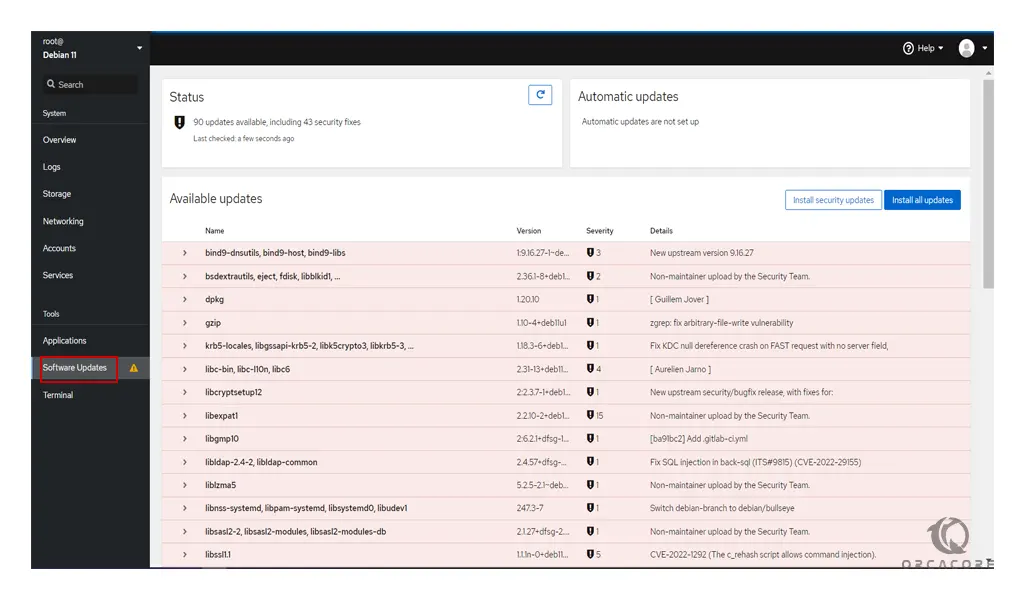
Click on the Software Updates. You should see all available updates.
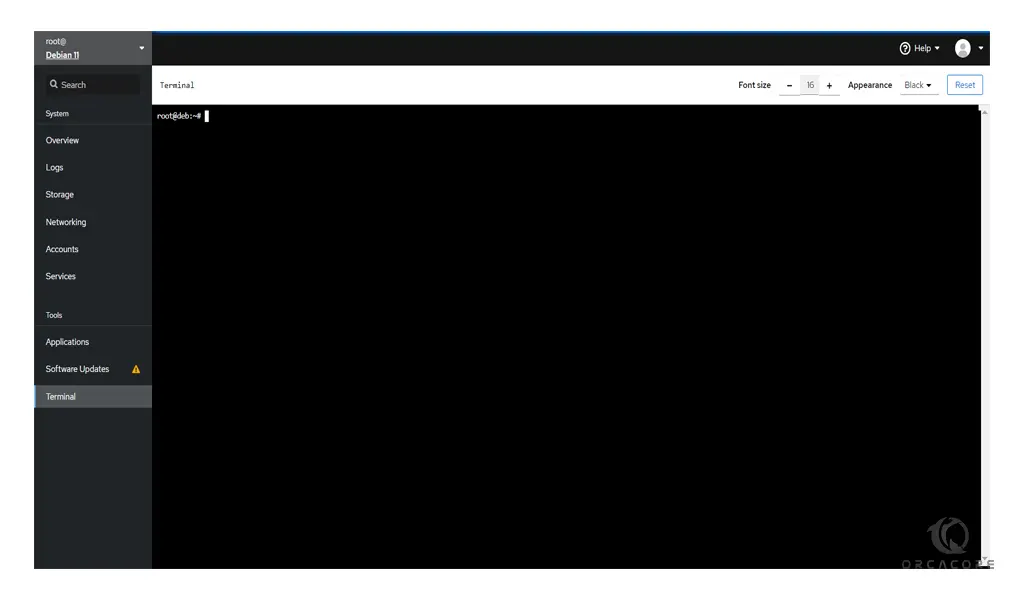
Also, you can connect to your server’s command-line interface by clicking on the Terminal.
For more information, you can visit the Cockpit Documentation page.
Conclusion
At this point, you learn to Install and Use Cockpit on Debian 11.
Hope you enjoy it.
You may be interested in these articles on the Orcacore website:
Set up Apache Maven on Debian 11



