Share your love
Install Nagios Monitoring Tool on Debian 11

In this guide, we want to teach you How To Install Nagios Monitoring Tool on Debian 11.
Nagios is an open-source monitoring system for computer systems. It was designed to run on the Linux operating system and can monitor devices running Linux, Windows, and Unix operating systems (OSes).
Nagios software runs periodic checks on critical parameters of application, network, and server resources. For example, Nagios can monitor memory usage, disk usage, microprocessor load, the number of currently running processes, and log files.
Also, it can monitor services, such as Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), and other common network protocols. Active checks are initiated by Nagios, while passive checks come from external applications connected to the monitoring tool.
How To Install Nagios Monitoring Tool on Debian 11
To install Nagios, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide the Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Now follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Set up Nagios Monitoring Tool on Debian 11
First, you must update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt update
Then, install the required packages and dependencies with the below command:
sudo apt install vim wget curl build-essential unzip openssl libssl-dev apache2 php libapache2-mod-php php-gd libgd-devAt this point, you must visit the Nagios Downloads page and get the latest release by using the following commands:
# NAGIOS_VER=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/NagiosEnterprises/nagioscore/releases/latest|grep tag_name | cut -d '"' -f 4)
# wget https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nagioscore/releases/download/$NAGIOS_VER/$NAGIOS_VER.tar.gzExtract your downloaded file:
tar xvzf $NAGIOS_VER.tar.gzNow you should compile your extracted file.
Switch to your Nagios directory with the following command:
cd $NAGIOS_VER
Begin the compile process by running the command below:
./configure --with-httpd-conf=/etc/apache2/sites-enabledWhen you are done, you will get the following output:
Output
...
Review the options above for accuracy. If they look okay,
type 'make all' to compile the main program and CGIs.Now you need to create a user and group. And the www-data user is also added to the “nagios” group.
# sudo make install-groups-users
Output
groupadd -r nagios
useradd -g nagios nagios
# sudo usermod -a -G nagios www-dataNow compile the main Nagios program and associated packages with the following command:
sudo make allThen, install the main program, CGIs, and HTML files:
sudo make installNext, install Nagios daemon files and also configures them to start when the system boots:
sudo make install-daemoninitAfter that, add the command mode that installs and configures the external command file:
sudo make install-commandmodeHere you should install SAMPLE configuration files required as Nagios needs some configuration files to allow it to start on Debian 11:
sudo make install-configConfigure Apache Web Server To Serve Nagios Web Pages
At this point, you need to configure our Apache to serve Nagios web pages. Nagios developers made it easier to set up Apache. You simply run one command to set up configuration files and then enable specific apache modules.
Install config files:
sudo make install-webconfEnable Apache rewrite and CGI modules:
sudo a2enmod rewrite cgiConfigure Nagios Apache Authentication
In this step, in order to create Nagios Web authentication, you need to create a web user for authentication. The “htpasswd” command rises to the occasion for this task. Please note that Nagios uses the “nagiosadmin” user by default. Run the command below and input your favorable password:
sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadminOutput
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user nagiosadminWhen you are done, set the correct permissions to the (/usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users) file with the following commands:
# sudo chown www-data:www-data /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users # sudo chmod 640 /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
Install Nagios Plugins on Debian 11
Before you can access to your Nagios web interface, you need Nagios Plugins that will help you accomplish a lot of stuff including monitoring the localhost. You can find the plugins at Nagios Plugins.
Now follow the steps below to install the latest plugins. First, switch to your home directory:
cd ~Then, run the following command to grab the Nagios plugins and extract it on Debian 11:
# VER=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/nagios-plugins/nagios-plugins/releases/latest|grep tag_name | cut -d '"' -f 4|sed 's/release-//') # wget https://github.com/nagios-plugins/nagios-plugins/releases/download/release-$VER/nagios-plugins-$VER.tar.gz # tar xvf nagios-plugins-$VER.tar.gz
Next, navigate into the new plugins folder then compile and install it:
# cd nagios-plugins-$VER # ./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios # sudo make # sudo make install
When you are done, you need to allow ports on the firewall and start Nagios.
# sudo ufw allow 80 # sudo ufw reload
Start Nagios and Apache services on Debian 11:
# sudo systemctl restart apache2 # sudo systemctl start nagios.service
Access Nagios Web Interface
At this point, you can access your Nagios web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by nagios:
http://<IP Address>/nagiosYou will be prompted for a username and password. The username as you may remember is the one we set in the previous steps, that is “nagiosadmin“. Provide credentials and click sign in.
Now you will see your Nagios dashboard:
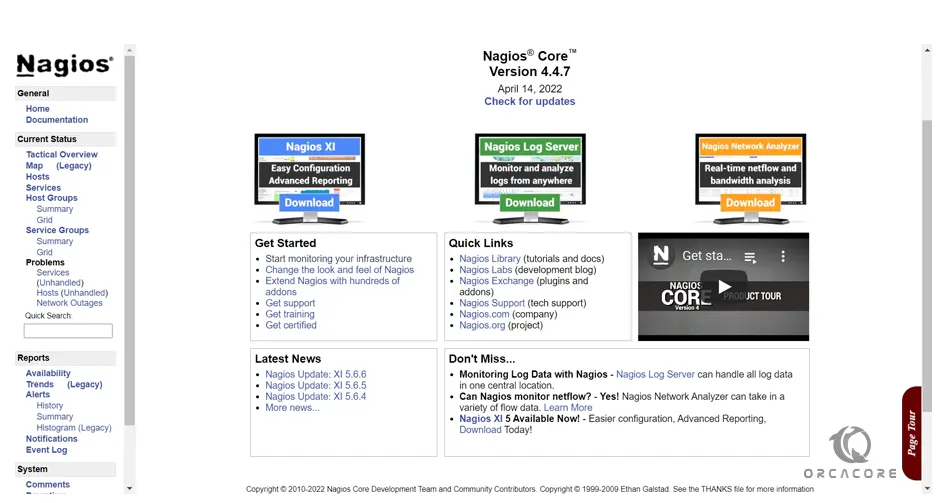
If you click on the “Hosts” link, you should see that the localhost is up and hence being monitored thanks to the plugins we installed earlier.
Conclusion
At this point, you learn to Install Nagios Monitoring Tool on Debian 11.
Hope you enjoy using it.
You may be interested in these articles:



