Share your love
Install Samba Share on Debian 11 – Full Guide Steps

This guide intends to show you how to Install Samba Share on Debian 11. Samba is an incredibly powerful tool that allows you to create seamless file and printer sharing to SMB/CIFS clients from a Linux server/desktop. With Samba you can even connect that Linux machine to a Windows Domain. But before you can tackle the more challenging aspects of Samba, you first must have it up and running.
Steps To Install Samba Share on Debian 11
To complete this guide, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Now follow the steps below to Install Samba Share on Debian 11.
Install Samba on Debian 11
Samba packages are available in the default Debian repository. First, update your local package index with the command below:
sudo apt updateThen, use the following command to Install Samba Share on Debian 11:
sudo apt install samba smbclient cifs-utilsThis will install the dependencies and required packages.
Configure Samba on Debian 11
At this point, you need to make some changes to the Samba config file and create shared Samba directories. To do these, follow the steps below.
Set Samba Global Settings
At this point, you need to open the Samba configuration file with your favorite text editor, here we use vi:
sudo vi /etc/samba/smb.confUnder the Global section, find the line below and make sure it is like this:
workgroup = WORKGROUPWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Create a Shared Samba Directory
At this point, you can share both public and private directories. So you can create the two directories by using the following commands:
# sudo mkdir /public
# sudo mkdir /privateNow you need to open the Samba config file again and add the shares and authentication methods to the end of the file.
sudo vi /etc/samba/smb.conf[public]
comment = Public Folder
path = /public
writable = yes
guest ok = yes
guest only = yes
force create mode = 775
force directory mode = 775
[private]
comment = Private Folder
path = /private
writable = yes
guest ok = no
valid users = @smbshare
force create mode = 770
force directory mode = 770
inherit permissions = yesWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Create a Samba Share User Group
At this point, you need the Samba share user group to access the Private share as specified in the config file above.
Create the group by using the command below:
sudo groupadd smbshareSet the correct permissions for the private share by using the commands below:
# sudo chgrp -R smbshare /private/
# sudo chgrp -R smbshare /publicNext, set the correct permissions for the directories:
# sudo chmod 2770 /private/
# sudo chmod 2775 /publicNote: The value 2 at the beginning of the above commands, stands for the SGID bit. This allows newly created files to inherit the parent group.
Now you should create a no-login local user to access the private share by using the command below:
sudo useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin sambauserThen, add the user to the Samba share group on Debian 11 with the following command:
sudo usermod -aG smbshare sambauserFinally, set a password for your Samba user:
sudo smbpasswd -a sambauserOutput
New SMB password:
Retype new SMB password:
Added user sambauser.Enable the created account by using the following command:
sudo smbpasswd -e sambauserOutput
Enabled user sambauser.Verify Samba Configuration
When you are done with the above steps, you can test whether your Samba configuration on Debian 11 is working correctly or not with the following command:
sudo testparmOutput
Load smb config files from /etc/samba/smb.conf
Loaded services file OK.
Weak crypto is allowed
Server role: ROLE_STANDALONE
Press enter to see a dump of your service definitions
# Global parameters
[global]
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
logging = file
map to guest = Bad User
max log size = 1000
obey pam restrictions = Yes
pam password change = Yes
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully* .
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
server role = standalone server
unix password sync = Yes
usershare allow guests = Yes
idmap config * : backend = tdb
[homes]
browseable = No
comment = Home Directories
create mask = 0700
directory mask = 0700
valid users = %S
[printers]
browseable = No
comment = All Printers
create mask = 0700
path = /var/spool/samba
printable = Yes
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
[public]
comment = Public Folder
force create mode = 0775
force directory mode = 0775
guest ok = Yes
guest only = Yes
path = /public
read only = No
[private]
comment = Private Folder
force create mode = 0770
force directory mode = 0770
inherit permissions = Yes
path = /private
read only = No
valid users = @smbshare
This means that everything is configured appropriately.
Create Demo Files in Samba Share
At this point, you can create demo files in the Samba shares. To do this. you can run the following commands:
# sudo mkdir /private/demo-private /public/demo-public
# sudo touch /private/demo1.txt /public/demo2.txtTo apply the changes, restart the Samba service on Debian 11:
sudo systemctl restart nmbdConfigure Firewall for Samba
If you have a firewall running, you need to allow remote access from the specified IP range as shown below:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.205.0/24 to any app SambaAccess Share Files From Local Machine
Before you set up Samba clients, you can try accessing your shared files with the command below on Debian 11:
smbclient '\\localhost\private' -U sambauserOutput
Enter WORKGROUP\sambauser's password:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Wed Jan 25 06:05:43 2023
.. D 0 Wed Jan 25 05:48:51 2023
demo1.txt N 0 Wed Jan 25 06:05:43 2023
demo-private D 0 Wed Jan 25 06:05:36 2023
51670492 blocks of size 1024. 47061244 blocks available
smb: \>
Set up Samba Share Windows Client
At this point, we want to show you access to the share from Windows. First, open a run box using Win+R, enter your Debian 11 IP address in the box, and click OK:
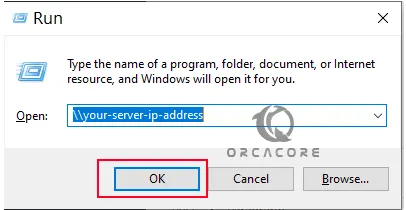
Then, the Samba shared folders on Debian 11 should appear as below:

You can open one of the files, and create a new file there. You should see the file on your server machine too.
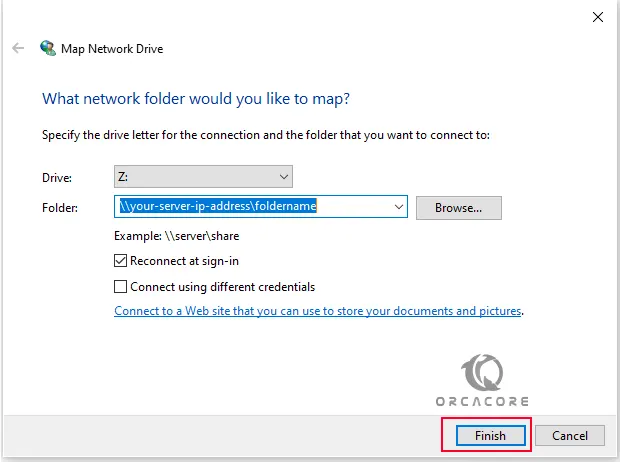
Mount Network Drive
At this point, you can mount the Samba share permanently on your Windows system. Click on This PC->Map Network Drive. This will open a window for you, provide the Path details, and click Finish.
Then, enter the Samba user credentials and click ok.
You will have the share available on your This PC.
Set up Samba Linux Client
At this point, you can access the shared folders from a Linux client. To do this, you need to have Samba packages installed on your server. Here our Linux client is Debian 11:
sudo apt install samba-client cifs-utilsThen, navigate to File Manager ->Other locations and add your share using the syntax below.
smb://server-name/Share_nameEnter the credentials for the Samba user. That is it! You have your Samba share on your Linux client machine.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Install Samba Share on Debian 11. Also, you have learned to set up Samba clients on both Windows and Linux machines.
Hope you enjoy it.
You may like these articles:



