Share your love
Install Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04

In this guide, we want to teach you to Install and Configure Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04.
Apache Kafka is a real-time data streaming technology capable of handling trillions of events per day. Initially conceived as a messaging queue, Kafka is based on an abstraction of a distributed commit log. Since being created and open-sourced in 2011, Kafka has since become the industry standard for working with data in motion.
Steps To Install Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04
To set up Apache Kafka, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Ubuntu 20.04.
Install Required Packages For Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04
First, you need to prepare your server for installing Kafka. Update and upgrade your local package index with the command below:
# sudo apt update
# sudo apt upgradeThen, use the command below to install the required packages, JRE, and JDK on Ubuntu 20.04:
sudo apt install default-jre wget git unzip default-jdk -ySet up Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04
At this point, you need to download and get the latest release of Kafka.
Download Kafka
Visit the Apache Kafka downloads page and look for the Latest release and get the sources under Binary downloads. Get one that is recommended by Kafka with the wget command:
sudo wget https://downloads.apache.org/kafka/3.3.2/kafka_2.13-3.3.2.tgzThen, make a directory for your Kafka under /usr/local directory and switch to it with the following commands:
# sudo mkdir /usr/local/kafka-server
# sudo cd /usr/local/kafka-serverNext, extract your downloaded file in this directory:
sudo tar -xvzf ~/kafka_2.13-3.3.2.tgz --strip 1Create Zookeeper Systemd Unit File
At this point, you need to create a Zookeeper systemd unit file for helping in performing common service actions such as starting, stopping, and restarting Kafka.
Zookeeper is a top-level software developed by Apache that acts as a centralized service and is used to maintain naming and configuration data and to provide flexible and robust synchronization within distributed systems. Zookeeper keeps track of the status of the Kafka cluster nodes and it also keeps track of Kafka topics, partitions, etc.
To create the zookeeper systemd unit file, you can use your favorite text editor, here we use the vi editor:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/zookeeper.serviceAdd the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=Apache Zookeeper Server
Requires=network.target remote-fs.target
After=network.target remote-fs.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/kafka-server/bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh /usr/local/kafka-server/config/zookeeper.properties
ExecStop=/usr/local/kafka-server/bin/zookeeper-server-stop.sh
Restart=on-abnormal
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Create Systemd Unit File for Kafka
Now you need to create a systemd unit file for Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04. To do this, use your favorite text editor, here we use vi:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/kafka.serviceAdd the following content to the file:
Note: Make sure your JAVA_HOME configs are well inputted or Kafka will not start.
[Unit]
Description=Apache Kafka Server
Documentation=http://kafka.apache.org/documentation.html
Requires=zookeeper.service
After=zookeeper.service
[Service]
Type=simple
Environment="JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64"
ExecStart=/usr/local/kafka-server/bin/kafka-server-start.sh /usr/local/kafka-server/config/server.properties
ExecStop=/usr/local/kafka-server/bin/kafka-server-stop.sh
Restart=on-abnormal
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Manage Kafka and Zookeeper Services
At this point, you need to reload the systemd daemon to apply changes and then start the services by using the commands below:
# sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# sudo systemctl enable --now zookeeper
# sudo systemctl enable --now kafkaVerify your Kafka and Zookeeper services are active and running on Ubuntu 20.04:
# sudo systemctl status kafkaOutput
● kafka.service - Apache Kafka Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/kafka.service; enabled; vendor preset:>
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-03-29 10:36:17 CEST; 37s ago
Docs: http://kafka.apache.org/documentation.html
Main PID: 5447 (java)
Tasks: 70 (limit: 4620)
Memory: 329.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/kafka.service
└─5447 /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java -Xmx1G -Xms1G -
...# sudo systemctl status zookeeperOutput
● zookeeper.service - Apache Zookeeper Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/zookeeper.service; enabled; vendor pre>
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-03-29 10:36:12 CEST; 1min 16s ago
Main PID: 5047 (java)
Tasks: 32 (limit: 4620)
Memory: 68.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/zookeeper.service
└─5047 java -Xmx512M -Xms512M -server -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseM>
...Install CMAK on Ubuntu 20.04
CMAK (previously known as Kafka Manager) is an open-source tool for managing Apache Kafka clusters developed by Yahoo. At this point, you need to clone the CMAK from GitHub by using the command below:
# cd ~
# sudo git clone https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK.gitOutput
Cloning into 'CMAK'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 6542, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (266/266), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (132/132), done.
remote: Total 6542 (delta 157), reused 201 (delta 122), pack-reused 6276
Receiving objects: 100% (6542/6542), 3.97 MiB | 13.67 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (4218/4218), done.
Configure CMAK on Ubuntu 20.04
At this point, you need to make some configuration changes in the CMAK config file. Open the file with your favorite text editor, here we use vi:
sudo vi ~/CMAK/conf/application.confChange cmak.zkhosts=”my.zookeeper.host.com:2181″ and you can also specify multiple zookeeper hosts by comma delimiting them, like so: cmak.zkhosts=”my.zookeeper.host.com:2181,other.zookeeper.host.com:2181“. The host names can be ip addresses too.
cmak.zkhosts="localhost:2181"When you are done, save and close the file.
At this point, you need to create a zip file that can be used to deploy the application. You should see a lot of output on your terminal as files are downloaded and compiled. This will take some time to complete.
# cd ~/CMAK/
# ./sbt clean distWhen it is completed, you will get the following output:
Output
[info] Your package is ready in /root/CMAK/target/universal/cmak-3.0.0.7.zipChange into the directory where the zip file is located and unzip it by using the commands below:
# cd /root/CMAK/target/universal # unzip cmak-3.0.0.7.zip # cd cmak-3.0.0.7
Access CMAK Service
When are finished with the previous step, you can run the Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka service on Ubuntu 20.04 by using the command below:
bin/cmakBy default, it will choose port 9000, so open your favorite browser and point it to http://ip-or-domain-name-of-server:9000. In case your firewall is running, kindly allow the port to be accessed externally:
sudo ufw allow 9000You should see the following interface:
Add Cluster From the CMAK
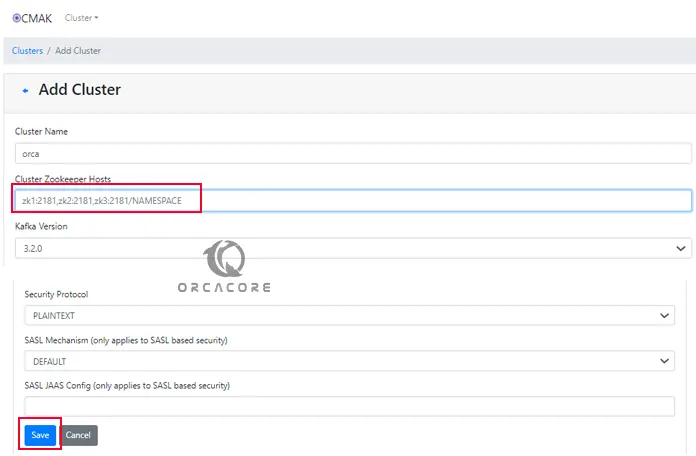
From there, you can easily add the clusters. To do this, click cluster, and add cluster.

You will be presented with a page as shown below. Fill in the form with the details being requested (Cluster Name, Zookeeper Hosts, etc). In case you have several Zookeeper Hosts, add them delimited by a comma. You can fill in the other details depending on your needs.
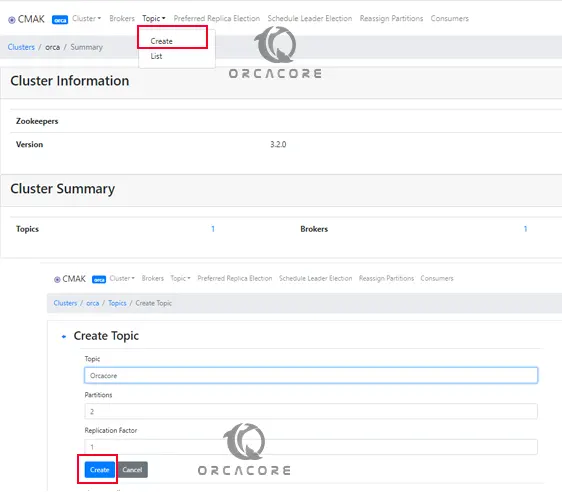
Create a Topic in the CMAK interface
From your newly added cluster on Apache Kafka Ubuntu 20.04, you can click on Topic, and create. You will be required to input all the details you need about the new Topic (Replication Factor, Partitions, and others). Fill in the form then click “Create”.
Then, click on Cluster view to see your topics.
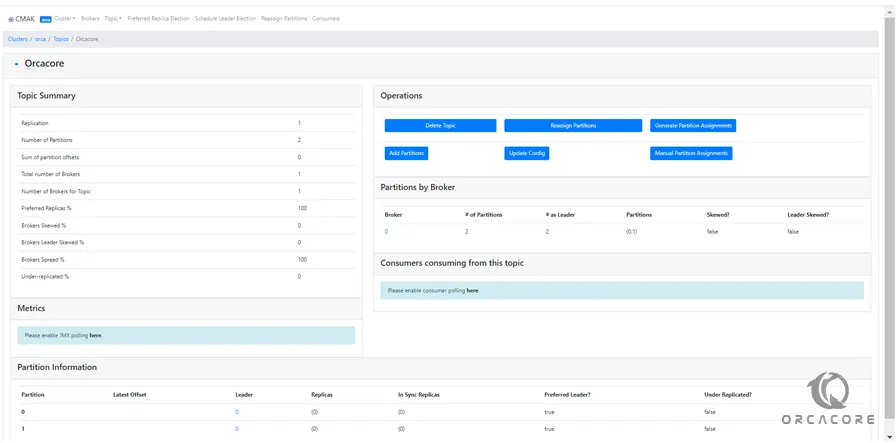
From there you can add topics, delete them, config them and etc.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Install and Configure Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 20.04.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these articles on the Orcacore website:



