Share your love
How To Install Cockpit on Centos 7

This tutorial intends to teach you How To Install the Cockpit on Centos 7.
The cockpit is a user-friendly web-based console that provides some very easy ways to administer Linux systems — through the web.
You can monitor system resources, add or remove accounts, monitor system usage, shut down the system and perform quite a few other tasks — all through a very accessible web connection. It’s also very easy to set up and use.
How To Install Cockpit on Centos 7
To install Cockpit, you need to log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide the Initial Server Setup with Centos 7.
Also, you need to set up a basic firewall. To do this, check our guide Set Up a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7.
Now follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Installing Cockpit on Centos 7
First, you need to update your local package index with the command below:
sudo yum update -y
The Cockpit packages are available in the default Centos repository. To install it, run the following command:
sudo yum install cockpit -y
Then, start and enable your Cockpit service on Centos 7 with the following commands:
# sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket # sudo systemctl start cockpit.socket
Now verify that Cockpit is active and running on your server by using the following command:
sudo systemctl status cockpit
Output cockpit.service - Cockpit Web Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.service; static; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-05-28 02:22:55 EDT; 2s ago Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8) Process: 22296 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/remotectl certificate --ensure --user=root --group=cockpit-ws --selinux-type=etc_t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 22300 (cockpit-ws) CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.service └─22300 /usr/libexec/cockpit-ws
At this point, you need to adjust the firewall for the Cockpit.
By default, Cockpit listens on port 9090. To allow Cockpit through the firewall, run the command below:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=cockpit
Reload the firewall, to apply the new rules:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Access Cockpit Web Interface
At this point, you can access Cockpit through the web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by:
http://server-ip-address:9090
You will see your Cockpit login screen. Enter your sudo username or root username and password—log in to proceed to the dashboard.
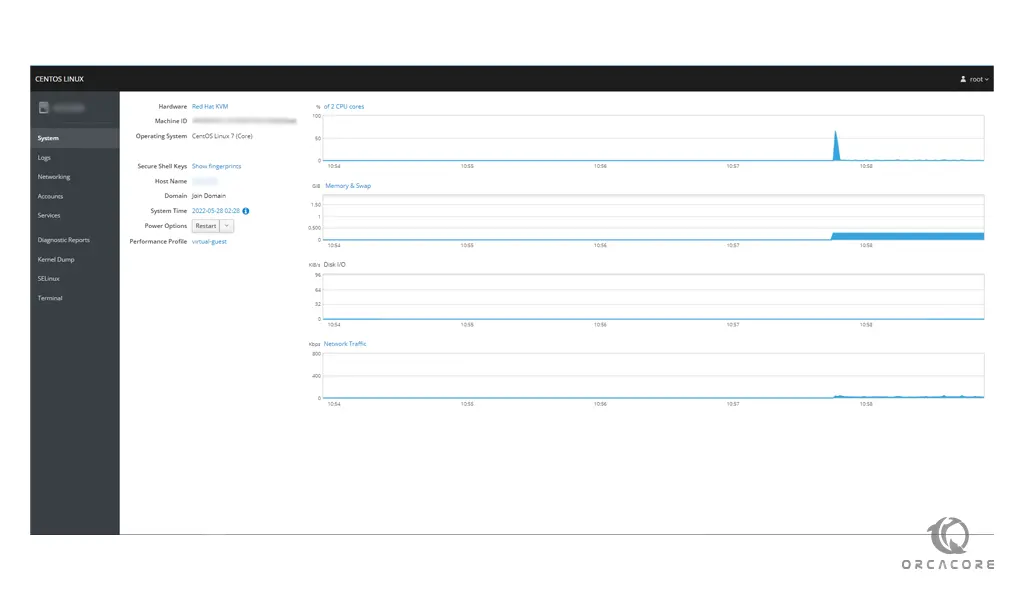
Once logged in, you will see the immediate dashboard. Cockpit’s main options are on the left side, where you can add additional hosts if they have SSH allow connections, view logs, configure network and containers, restart, kill and maintain services and much more.
One of the main benefits of using Cockpit is having a terminal screen in a Web UI. At the bottom of the page, click Terminal.
From there, you have a terminal with the power of using a Web-based GUI to assist you in bringing the best of both worlds together.
Conclusion
At this point, you learn to Install Cockpit on Centos 7.
Hope you enjoy it.
May this article on the orcacore website be useful for you:



