Share your love
Install and Configure Django on Debian 11

In this article, we want to teach you How To Install and Configure Django on Debian 11.
Django is a free and open-source web application framework, written in Python. A web framework is a set of components that helps you to develop websites faster and easier.
How To Install and Configure Django on Debian 11
Before you start to install Django on Debian 11, you need to log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our article the Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Now follow the steps below to install Django on Debian 11.
Install Pip on Debian 11
To install Django, you need to have Pip installed on your Debian 11.
First, update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt update
Then, use the following command to install Pip 3 on Debian 11:
sudo apt install python3-venv python3-pipVerify your Pip installation by checking its version:
pip3 --version
In your output you will see:
Output
pip 20.3.4 from /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pip (python 3.9)
Set up Django on Debian 11
Here you can install Django on your server in the user space and globally.
To install Django in the user space, run the following command:
sudo pip3 install --user Django
You can use the following command to install Django globally:
sudo pip3 install DjangoWhen your installation is completed, in your output you will see:
Output
Successfully installed Django-4.0 asgiref-3.4.1 sqlparse-0.4.2
The installation of Django will provide you with the Django-admin tool to manage the projects.
which django-admin
Output
/usr/local/bin/django-admin
Also, you can check your Django installation by checking its version:
django-admin --version
Output
4.0
Create a Django test app on Debian 11
At this point, we will show you how to create a Django test app.
First, create a directory and switch to it with the command below:
sudo mkdir project && sudo cd project
Then, use the Django-admin tool to start a project named test_app, you can choose your own name:
django-admin startproject test_app
Switch to your Django project directory:
cd test_appNow you can use Python 3 to apply pending migrations:
python3 manage.py migrate
In your output you will see:
Output
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying contenttypes.0001_initial... OK
Applying auth.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0002_logentry_remove_auto_add... OK
Applying admin.0003_logentry_add_action_flag_choices... OK
Applying contenttypes.0002_remove_content_type_name... OK
Applying auth.0002_alter_permission_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0003_alter_user_email_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0004_alter_user_username_opts... OK
Applying auth.0005_alter_user_last_login_null... OK
Applying auth.0006_require_contenttypes_0002... OK
Applying auth.0007_alter_validators_add_error_messages... OK
Applying auth.0008_alter_user_username_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0009_alter_user_last_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0010_alter_group_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0011_update_proxy_permissions... OK
Applying auth.0012_alter_user_first_name_max_length... OK
Applying sessions.0001_initial... OK
Create a Django Admin user on Debian 11
Here you need to create an Admin user for your Django project. From your Django project directory on Debian 11, run the following command to create your superuser:
python3 manage.py createsuperuser
You need to enter your Email address, username, and password to create your superuser.
Output
Username (leave blank to use 'olivia'): admin
Email address: olivia@orcacore.com
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully.
Access Django Web Application
By default, Django doesn’t allow external access to the application. If you want to allow external access you can open your test app settings file with your favorite text editor, here we use vi:
sudo vi test_app/settings.py
Search for the ALLOWED_HOSTS line and set it to your host IP.
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['host-ip']When you are done, save and close the file.
Now you can start your Django project on Debian 11 with the command below:
python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080
In your output you will see:
Output
Watching for file changes with StatReloader
Performing system checks...
System check identified no issues (0 silenced).
January 01, 2022 - 08:57:33
Django version 4.0, using settings 'test_app.settings'
Starting development server at http://0.0.0.0:8080/
Quit the server with CONTROL-C.
Now in your web browser type your server’s IP address followed by 8080:
http://[server IP/hostname]:8080
You will see the successfully installed message:
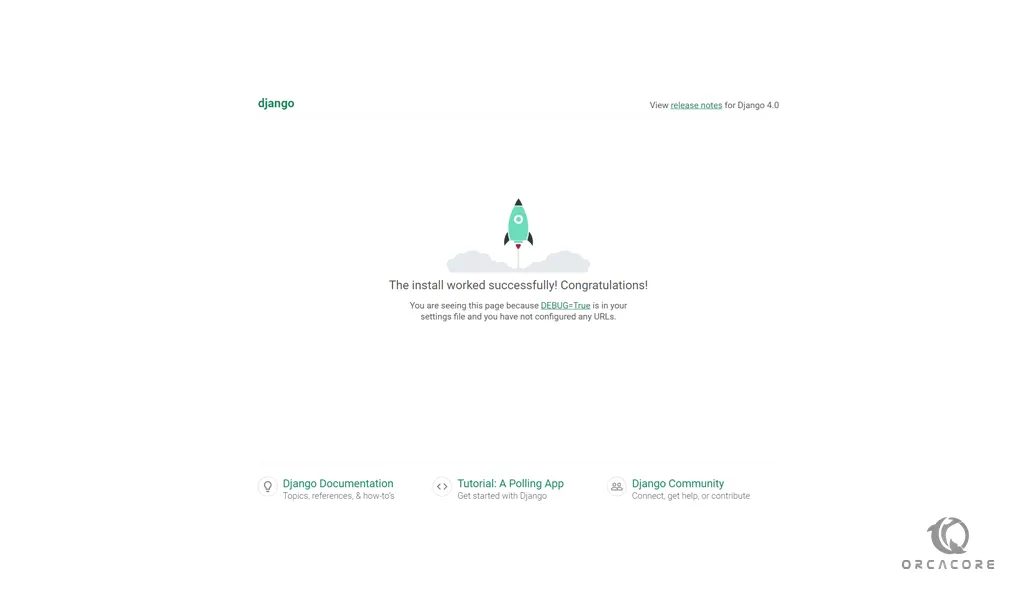
To access the Django admin login page, enter your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 8080/admin:
http://[server IP/hostname]:8080/admin
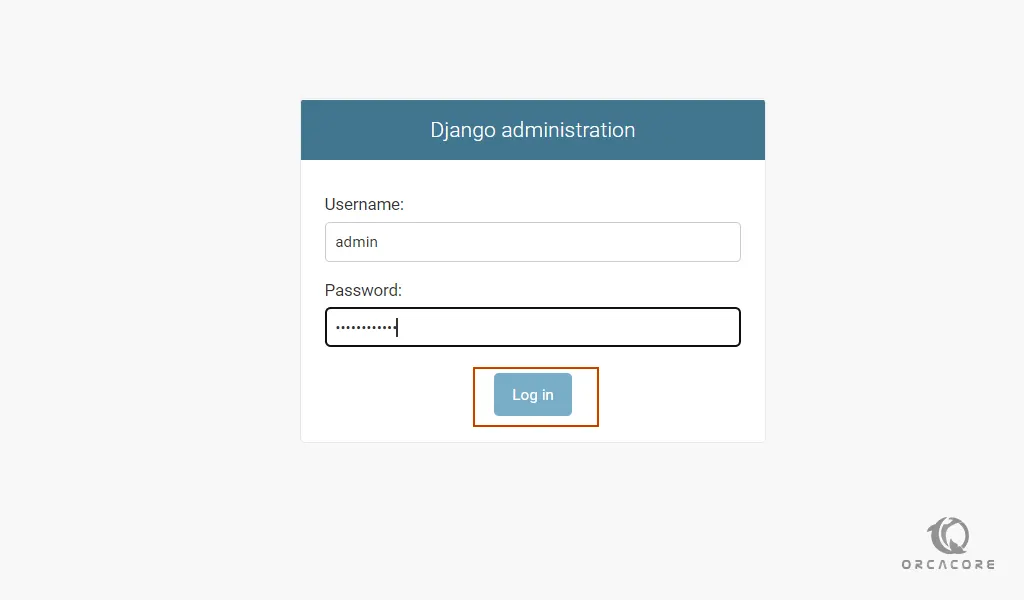
Enter your admin user and password that you have set before and press login.
You will see the Django Admin dashboard:
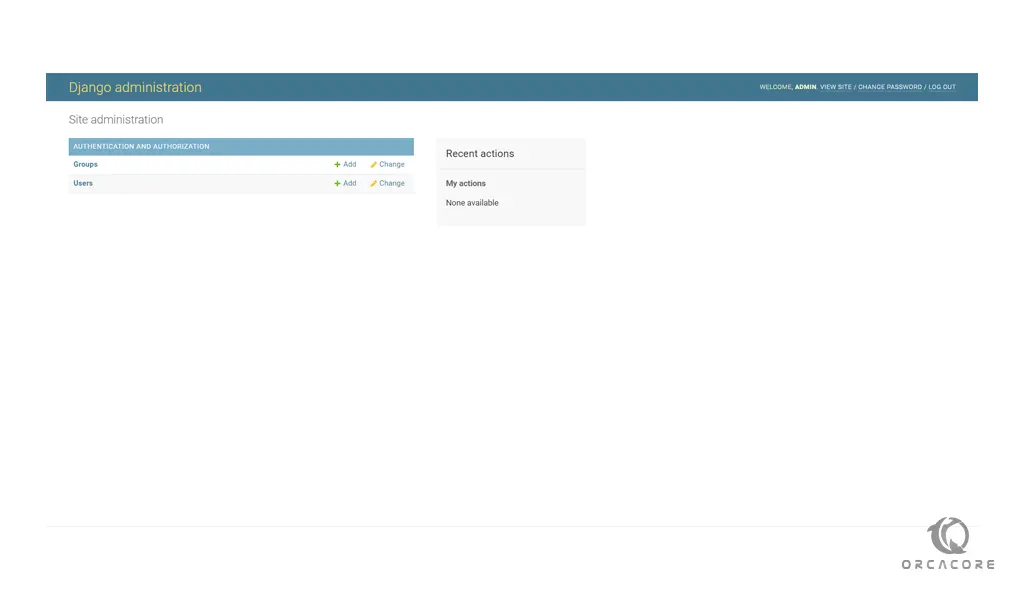
Conclusion
At this point, you learn to install Django on Debian 11.
Hope you enjoy using it.
Also, the below link helps you install Django on other Linux distros:
Install Django on Rocky Linux 9
Install Django on Ubuntu 22.04
Install and Configure Django on AlmaLinux 8
For more information, you can visit the Django Documentation page.



