Share your love
How To Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04

In this tutorial, we want to teach you How To Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04.
Cockpit is a free and open-source web-based system management application. It is actively being developed by Red Hat. Using Cockpit, anyone can easily monitor and manage multiple servers at the same time via a Web browser. It will perfectly be suitable for new system administrators to perform simple tasks such as storage administration, inspecting journals, and starting and stopping services.
On the other hand, a service started from the Terminal can also be stopped or monitored from the Cockpit and vice versa. Also, if an error occurs in the terminal, it can be seen in the Cockpit journal interface.
Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04
To install Cockpit, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide the Initial Server Setup with Ubuntu 22.04.
Now follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Set up Cockpit Administration Tool on Ubuntu 22.04
By default, the Cockpit packages are available in the default Ubuntu repository. First, update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt update
Then, use the following command to install Cockpit on your server:
sudo apt install cockpit -y
Next, start your Cockpit service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start cockpit.socket
Enable it to start on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable cockpit.socket
Now verify your Cockpit service is active and running on Ubuntu 22.04 with the command below:
sudo systemctl status cockpit.socketOutput ● cockpit.socket - Cockpit Web Service Socket Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket; enabled; vendor preset> Active: active (listening) since Sun 2022-06-26 13:17:52 CEST; 21s ago Triggers: ● cockpit.service Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8) Listen: [::]:9090 (Stream) Tasks: 0 (limit: 2282) Memory: 1.2M CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.socket
At this point, you need to configure the firewall for Cockpit. We assumed that the UFW firewall is installed and configured on your system then you will need to allow ports 80 and 9090 through the UFW firewall. To do this, run the commands below:
# sudo ufw allow 9090 # sudo ufw allow 80
Then, reload the firewall to apply the new rules:
sudo ufw reload
You can check your UFW firewall status with the following command:
sudo ufw status
Output
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
9090 ALLOW Anywhere
80 ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
9090 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)Access Cockpit Web Interface
At this point, you can access the Cockpit web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 9090:
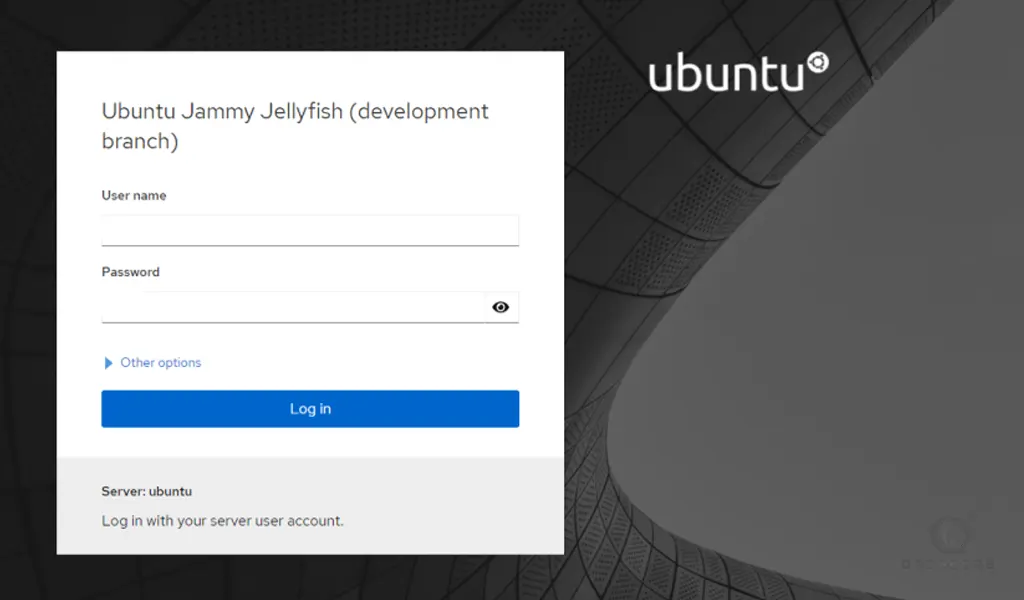
http://your-server-ip:9090You should see the Cockpit login screen. Provide your root username, and password and click on Login.
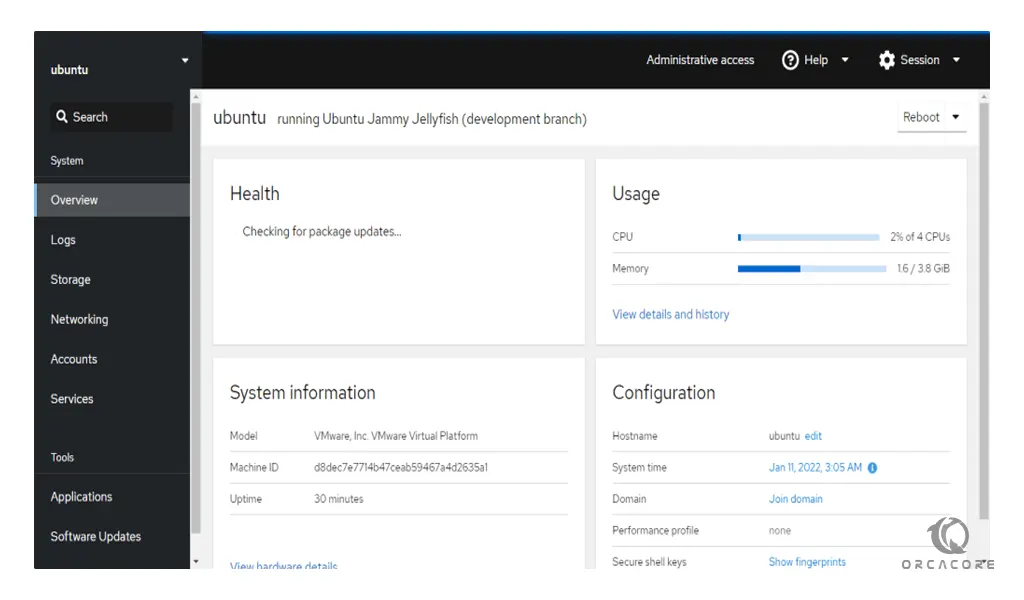
Now you will see your Cockpit dashboard. The first screen that comes is Overview– for shows various information such as CPU and Memory Usage; System health and configuration; hardware information.
To see your system’s partition information, click on Storage in the left pane.
Also, you can see the network-related information by clicking on Networking.
Click on the Services. You should see all system services.
From the Applications, you should see all installed applications.
Click on the Software Updates. You should see all available updates.
Also, you can connect to your server’s command-line interface by clicking on the Terminal.
Conclusion
Cockpit is a powerful and lightweight tool that can help users to configure their systems faster. It is not meant to replace configuration management tools like Ansible, but it helps to simplify trivial tasks. It doesn’t get in the way, break configuration files, or impose any opinion, and it has security in mind.
Hope you enjoy this guide How To Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04.
You may be interested in these articles:
How To Install Django on Ubuntu 22.04
Install and Use Rust Programming Language on Ubuntu 22.04



