Share your love
Install Monit Manager on Debian 11

In this guide, we want to show you to Install Monit Manager on Debian 11.
Monit is a helpful program that automatically monitors and manages server programs to ensure that they not only stay online consistently, but that the file size, checksum, or permissions are always correct. Additionally, Monit comes with a basic web interface through which all of the processes can be set up.
Steps To Install Monit Manager on Debian 11
To complete this guide, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Install Monit o Debian 11
The Monit packages are available in the default Debian 11 repository. First, update your local package index with the command below:
# sudo apt update
# sudo apt upgrade -yThen, use the following command to install the Monit:
sudo apt install monit -yManage Monit Service
At this point, your Monit service should be activated on your server. To check the status of Monit, run the command below:
sudo systemctl status monit --no-pager -lOutput
● monit.service - LSB: service and resource monitoring daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/monit; generated)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-03-20 08:09:59 EDT; 13s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 24901 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/monit start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4679)
Memory: 1.6M
CPU: 25ms
CGroup: /system.slice/monit.service
└─24911 /usr/bin/monit -c /etc/monit/monitrc
...If your service wasn’t started, use the following command:
sudo systemctl start monitAlso, you can check your Monit version:
sudo monit --versionOutput
This is Monit version 5.27.2
Built with ssl, with ipv6, with compression, with pam and with large files
Copyright (C) 2001-2020 Tildeslash Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Configure Monit Service Manager on Debian 11
The Monit program can be configured using the /etc/monit/monitrc file. It is recommended that you do not make your own settings directly in this file. It is better to create a new one for the desired settings.
Enable Monit httpd port
By default, port 2812 is disabled which is used for communicating with Monit. So you need to enable it. To do this, open the Monit config file by using your favorite text editor, here we use the vi editor:
sudo vi /etc/monit/monitrcFind the line: set httpd port 2812
There remove the # tag for the following lines. Also, replace the allow and use address value from localhost to 0.0.0.0 if you want to access the Monit web interface remotely as shown below.
You can also change the default password for the admin that is monit.
set httpd port 2812 and
use address 0.0.0.0 # only accept connection from localhost (drop if you use M/M>
allow 0.0.0.0/0 # allow localhost to connect to the server and
allow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit'When you are done, save and close the file.
To check the Monit configuration, use the command below:
sudo monit -tOutput
Control file syntax OKEnable Monit Service Manager
By default, the Monit service is not enabled on Debian 11. To enable the Monit service to get started automatically with the system boot, run the command below:
sudo /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable monitTo apply the changes, restart the service:
sudo systemctl restart monitAlso, you can check that everything is working correctly by using the command below:
sudo monit statusOutput
Monit 5.27.2 uptime: 0m
System 'deb.orca'
status OK
monitoring status Monitored
monitoring mode active
on reboot start
load average [0.00] [0.00] [0.00]
cpu 0.0%usr 0.0%sys 0.0%nice 0.0%iowait 0.0%hardirq 0.0%softirq 0.0%steal 0.0%guest 0.0%guestnice
memory usage 283.6 MB [7.2%]
swap usage 0 B [0.0%]
uptime 2d 1h 56m
boot time Sat, 18 Mar 2023 06:19:53
filedescriptors 608 [0.0% of 9223372036854775807 limit]
data collected Mon, 20 Mar 2023 08:15:56
Configure Firewall for Monit
At this point, you need to allow port 2812 through the UFW firewall. To do this, run the command below:
sudo ufw allow 2812Reload the firewall to apply the new rules:
sudo ufw reloadAccess Monit Service Manager Web Interface
At this point, you can access your Monit web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 2812:
http://your-server-ip-address:2812You will see the sign-in screen. Enter the admin user and password you have defined in the Monit config file and click Sign in.
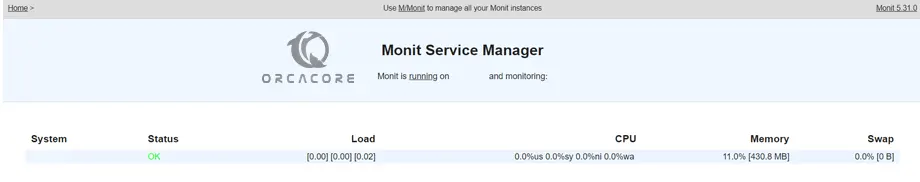
You will see the following screen:
Add Services In Monit on Debian 11
At this point, you can create a service file for an application to get monitored or can use the pre-configured ones available in the M/Monit folder.
In the /etc/monit/conf-available/ there are several ready-made files for various common server services such as:
acpid, at, mdadm, mysql, openntpd, pdns-recursor, rsyslog, snmpd,
apache2, cron, memcached, nginx, openssh-server, postfix and smartmontools.In order for Monit to take over the settings for the desired service, a soft link to the service file must be created and activated in the /etc/monit/conf-enabled/.
For example, you want to monitor Nginx using its pre-configured file. To do this, you can use the command below:
sudo ln -s /etc/monit/conf-available/nginx /etc/monit/conf-enabled/Then, reload the Monit service:
sudo monit reloadIn your Monit service manager, you should see:
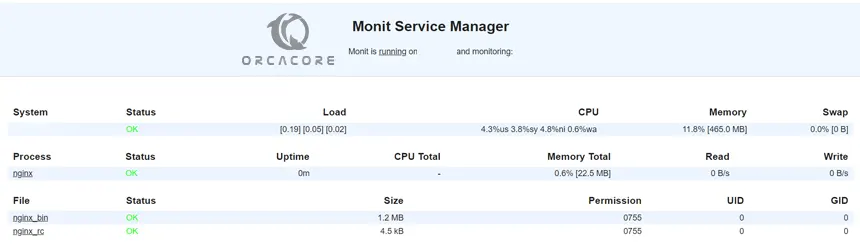
If you want to add another service that is not in the ready-made file, you can add it manually.
For example, If you want to detect all information about your system hardware using sensors, you can install it by using the command below:
sudo apt install lm-sensors -yThen, you need to create the file for it:
sudo vi /etc/monit/conf-available/sensorsAdd the following content to it:
check program sensors with path /usr/bin/sensors
if status != 0 then alertWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Next, enable it by using the command below:
sudo ln -s /etc/monit/conf-available/sensors /etc/monit/conf-enabled/Finally, reload the Monit service on Debian 11:
sudo monit reloadThat’s it, you are done.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Install and Configure Monit Service Manager on Debian 11. Also, you have learned to add services to be monitored on Monit.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these articles:
How To Set up Adminer on Debian 11



