Share your love
How To Set up Adminer on Debian 11

In this guide, we want to teach you to Set up or Install Adminer on Debian 11.
Adminer is a tool for managing the contents of MySQL databases, formerly known as phpMinAdmin. It’s a single tiny PHP file.
Adminer provides:
- An easy-to-use interface.
- Better support for many MySQL features.
- A more remarkable performance.
- Increased security.
Unlike phpMyAdmin, which only supports the management of MySQL and MariaDB databases, Adminer also supports managing other databases such as PostgreSQL, SQLite, MS SQL, Oracle, SimpleDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, and Firebird. It is also available in 43 languages.
Steps To Set up Adminer on Debian 11
To complete this guide, log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Also, you need to have LAMP Stack installed on your server. For this purpose, you can follow our guide on How To Install LAMP Stack on Debian 11.
Set root Database password for Adminer
When you are done with the requirements, run the command below to install an additional PHP extension:
sudo apt install php-curl libapache2-mod-php php-cli php-mysql php-gd -yThen, you need to set a root database password for Adminer. This will help you to manage all available databases using Adminer. To do this, log in to your MariaDB shell:
sudo mysql -u root -pNow, set the password for the root user with the command below:
MariaDB [(none)]> SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD("password");Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB shell:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> exit;Install Adminer on Debian 11
Adminer packages are available in the default Debian repository. You can easily install it by using the command below:
sudo apt install adminer -yThen, enable the Apache configuration file for Adminer on Debian 11:
sudo a2enconf adminerFinally, restart Apache to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Access Adminer Web Interface
At this point, you can access the Adminer web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by /adminer:
http://server-ip-address/adminerYou will see the Adminer Login screen. You should enter the root as the username and the password that you have configured for the Adminer.
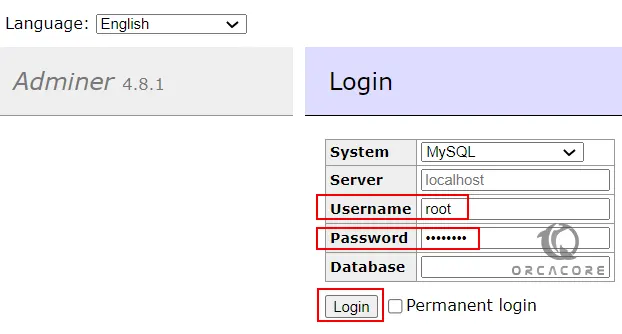
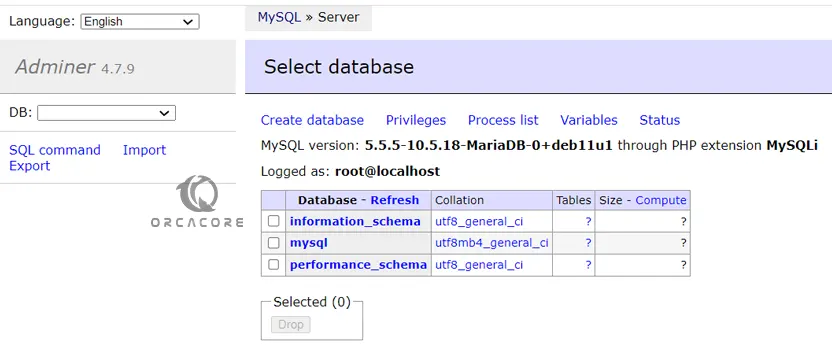
After login, you will have the Dashboard to access all the available databases. You can delete or create a database as well. However, the interface of Amdiner is not rich as that of PhpMyAdmin, yet simple, easy to navigate, understandable, and not confusing.
Uninstall Adminer from Debian 11
If you don’t want the Adminer Database system manager anymore on your Debian system; then you can remove it completely by using the commands below:
sudo apt autoremove --purge adminerThose who also want to uninstall Apache, MariaDB, and PHP, use the following commands:
sudo systemctl stop apache2 mariadbsudo apt autoremove --purge mariadb-server php* apache2Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Set up or Install Adminer on Debian 11.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these articles:



