Share your love
Install and Run Cockpit on Debian 12 Bookworm

In this guide, you will learn to Install and Run Cockpit on Debian 12 Bookworm. Cockpit is a web-based system management and monitoring tool that is available for free. You can follow this instruction to install and access the Cockpit dashboard on Debian 12 Bookworm.
How To Install and Run Cockpit on Debian 12 Bookworm?
Before you start your Cockpit installation, you must have access to your server as a non-root user and set up a basic UFW firewall. For this purpose, you can visit this guide on Initial Server Setup with Debian 12 Bookworm.
Then, follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Step 1 – Install Cockpit on Debian 12 Bookworm
Cockpit packages are available in the Linux distributions by default. First, run the system update with the following command:
sudo apt updateThen, run the following command on your Debian server to install Cockpit:
sudo apt install cockpit -y
Step 2 – How To Start Cockpit Service on Debian 12?
Now that you have installed Cockpit, you can use the command below to start your service:
sudo systemctl start cockpit.socket
Enable your Cockpit service to start on the boot system with the command below:
sudo systemctl enable cockpit.socket
Verify your Cockpit service is active and running on Debian 12 by running the following command:
sudo systemctl status cockpit.socketIn your output, you should see:
Output
● cockpit.socket - Cockpit Web Service Socket
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket; enabled; preset: enabl>
Active: active (listening) since Thu 2023-08-17 07:45:29 EDT; 58s ago
Triggers: ● cockpit.service
Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8)
Listen: [::]:9090 (Stream)
Tasks: 0 (limit: 4644)
Memory: 8.0K
CPU: 21ms
CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.socket
...Step 3 – Configure UFW Firewall Rules for Cockpit
Here we assumed that you have enabled UFW from the initial Debian 12 setup. At this point, you need to allow the Cockpit port which is 9090 through the firewall. Also, you need to allow port 80. To do this, run the following UFW commands:
# sudo ufw allow 9090
# sudo ufw allow 80Reload the firewall to apply the new rules:
sudo ufw reloadYou can verify your UFW status with the command below:
sudo ufw statusOutput
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
9090 ALLOW Anywhere
80 ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
9090 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Tips: To get more information about UFW rules, you can visit this guide on Configure Firewall with UFW on Debian 12 Bookworm.
Step 4 – Access Cockpit Console via Web Interface
At this point, you have run your Cockpit service on Debian 12 Bookworm. Now you can access your dashboard by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 9090:
http://your-server-ip:9090
You will see the Cockpit Login screen. You need to enter your root user and password and click Login:
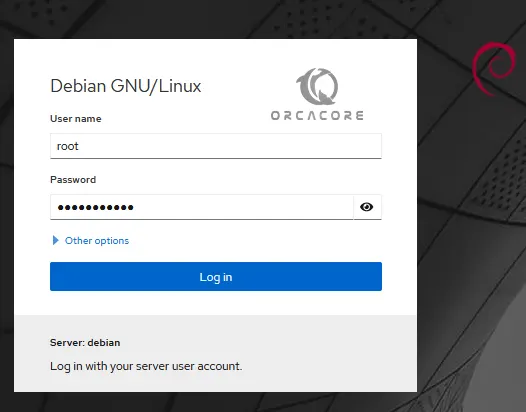
Can not log in to Cockpit by the default root user on Debian 12
If you see the message error like the following in your login screen:
Wrong user name or passwordYou can fix this issue by editing the /etc/cockpit/disallowed-users file. Open the file, with your favorite text editor, here we use the vi editor:
sudo vi /etc/cockpit/disallowed-usersAt the file, remove the root entry. With this option, you allow the root login to Cockpit.
When you are done, save and close the file.
Then, restart your Cockpit service:
sudo systemctl restart cockpit.socketNow try to connect your Cockpit with root credentials and it works correctly.
At this point, you should see your Cockpit dashboard on Debian 12:
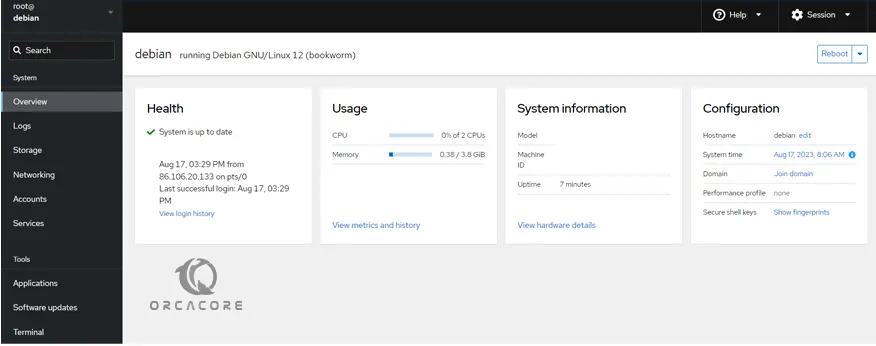
As you can see from the dashboard menu, you can view and manage Logs, Storage, Networking, Accounts, services and etc. Also, it gives you a terminal-based interface where you can run commands from there.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Install and Run Cockpit on Debian 12 Bokworm from the APT repository and access your Cockpit dashboard. Also, if you got an error while logging in with root to your Cockpit console, you can easily fix it by removing the root entry from the /etc/cockpit/disallowed-users file.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these articles too:



