Share your love
Installing PostgreSQL on Debian 13 Trixie

Installing PostgreSQL on Debian 13 Trixie has a straightforward process, which allows you to access the Postgres shell. As described on the official website, PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system that uses and extends the SQL language, combined with many features that safely store and scale the most complicated data workloads.
In this tutorial from the Orcacore website, you can easily install and manage PostgreSQL on Debian 13 Trixie and create a new PostgreSQL role and database, and access the Postgres shell with the new role.
Table of Contents
Install and Configure PostgreSQL 17 on Debian 13
To install PostgreSQL on Debian 13, log in to your server as a root or non-root user with sudo privileges and proceed to the guide steps below to start your installation setup.
What version of Postgres is Debian 13?
PostgreSQL version 17 is available in the default Debian 13 repository. You can easily access the Postgres 17 shell by following this guide steps.
Installing PostgreSQL on Debian 13 Trixie
As we said, Debian 13 Trixie ships with the latest version of PostgreSQL, which is Postgres 17. First, run the system update and install PostgreSQL 17 with the following commands:
# sudo apt update
# sudo apt install postgresql -yDuring the installation, PostgreSQL will be activated. You can verify it by using the command below:
sudo systemctl status postgresqlIn the output, you must see:
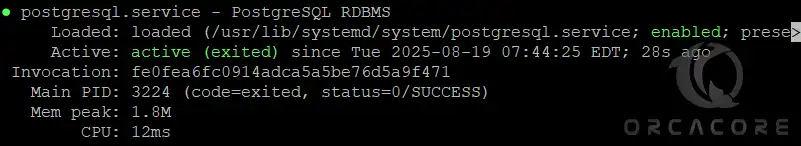
If the service is not enabled, you can enable it by using the command below:
sudo systemctl enable postgresql --nowYou can also manage your PostgreSQL database server from the command line by using the following commands:
sudo systemctl start postgresql #Start PostgreSQL-Service
sudo systemctl stop postgresql #Stop PostgreSQL-Service
sudo systemctl restart postgresql #Restart PostgreSQL-Service
sudo systemctl reload postgresql #Reload PostgreSQL-Service
sudo systemctl status postgresql #Check PostgreSQL-Service StatusAccess Postgres Shell
During the PostgreSQL installation, Postgres is set up to use ident authentication, meaning that it associates Postgres roles with a matching Unix/Linux system account. You can easily switch to the Postgres account with the command below:
su postgresYour login shell will change to Postgres. Then, you can access the Postgres shell with the following command:
psql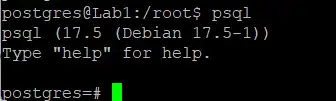
You can exit from the Postgres shell with the command below:
\qAdd PostgreSQL Role
From the Postgres account, you can use the command below to add a new PostgreSQL role:
createuser --interactiveEnter the name of the role and make it a superuser.

Add PostgreSQL Database
The Postgres authentication system for any role used to log in, the role should have a database with the same name that it can access. So use the command below to create the database with the same name as the PostgreSQL role:
createdb orcacoreAt this point, you must return to your regular Linux user by typing exit:
exitRun Postgres Shell with New Role
You must create a new Linux user with the same name as the PostgreSQL role:
sudo adduser orcacoreOnce you are done, connect to the Postgres shell with the following commands:
su - orcacore
psqlWhen you have logged in to your database, you can check your current connection information by running the following command:
\conninfo psql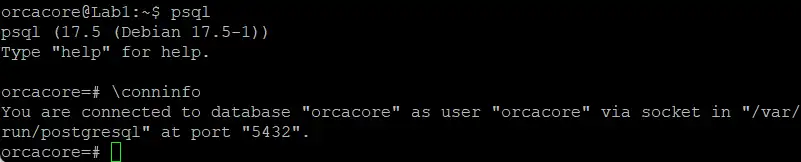
That’s it, you are done. For more detailed information, you can check the official Docs page.
FAQs
How can I check if PostgreSQL is running?
Check your PostgreSQL service status by using the command below:sudo systemctl status postgresql
What’s the default way to log in to the PostgreSQL shell?
Switch to the postgres system user and use psql:sudo -u postgres psql
Where is PostgreSQL’s configuration stored on Debian 13?
Main configuration files are in:/etc/postgresql/17/main/postgresql.conf – main settings (e.g., listen addresses, memory)pg_hba.conf – authentication rules (local/remote connections)
Which port does PostgreSQL use by default?
PostgreSQL’s default port is 5432.
Conclusion
Debian 13 provides a stable and secure environment for PostgreSQL 17. Installing and accessing PostgreSQL 17 on Debian 13 is a straightforward process. With just a few commands, you can set up the latest version, verify its status, and start working inside the database using the psql shell.
Hope you enjoy it. Please subscribe to us on Facebook, X, and YouTube.
You may also like to read the following articles:
How to Upgrade Debian 12 Bookworm to Debian 13 Trixie



