Share your love
Network Monitoring with OpManager on Debian 12

Network Monitoring is one of the most important tasks that every administrator must do, you can easily use the OpManager Tool on Debian 12 Bookworm to detect and resolve issues. This tool is provided by ManageEngine and with this tool, you can monitor any network device including servers, switches, routers, printers, WLAN controllers, VMs, firewalls, etc.
Learn Network Monitoring with OpManager on Debian 12 Bookworm
You can easily set up OpManager from the command line interface. Before you start, you must have access to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can check the Initial Server Setup with Debian 12.
Now proceed to the following steps to complete this guide.
Step 1 – Download OpManager Installer Script on Debian 12
ManageEngine website provides an installer script for Linux distros that you can use to install OpManager. To do this, visit the official downloads page and use the following wget command to download the standard edition script. This has a 30-day trial version. Also, you can purchase the enterprise version or use the free version that can be used for 3 devices.
sudo wget https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/29809517/ManageEngine_OpManager_64bit.binWhen your download is completed, make your file executable by using the following command:
sudo chmod u+x ManageEngine_OpManager_64bit.bin
Step 2 – Run OpManager Network Monitoring Installer Script
At this point, you can simply start your OpManager installation by running the following script:
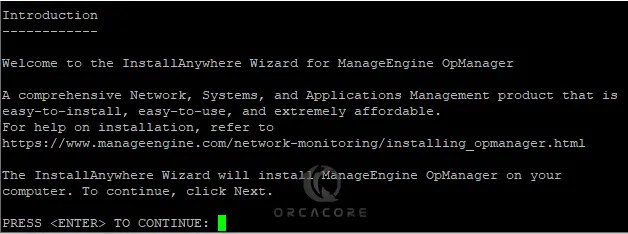
sudo ./ManageEngine_OpManager_64bit.binFirst, press continue to read the terms and conditions.
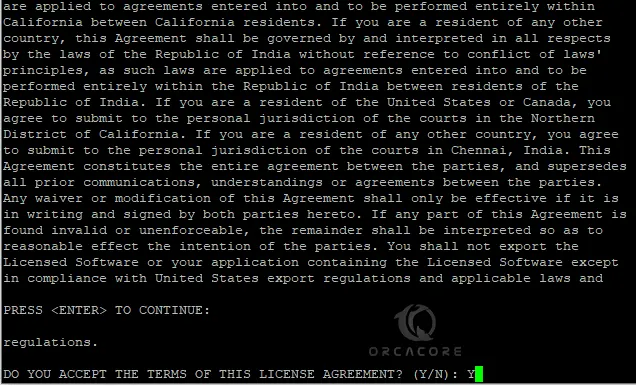
Then, press Y to accept the terms and services.
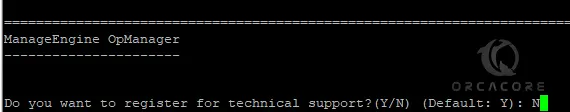
Next, can register for technical support. Press Y or N as you wish.
Now you must enter the installation directory or accept the default folder.

The default port used by the OpManager web server is 8060 for HTTP and 8061 for HTTPS. You can change it or accept the default.
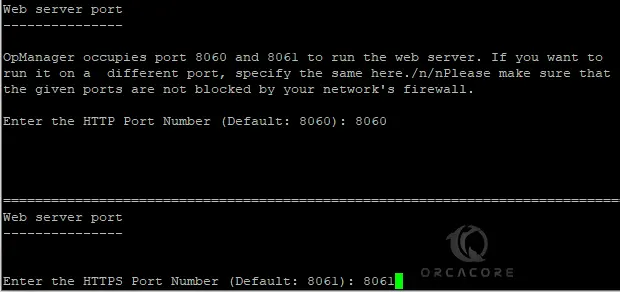
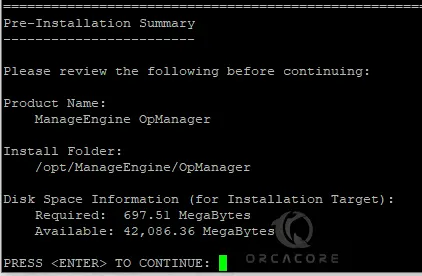
Read your pre-installation summary of OpManager on Debian 12 and press Continue.
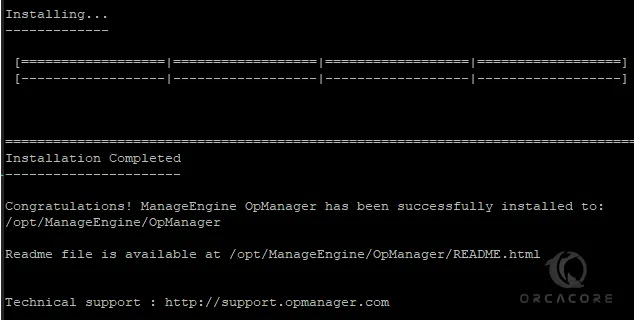
Once your installation is completed, you will get the following output:
Step 3 – Start OpManager Service on Debian 12
At this point, you can start your OpManager network monitoring tool on your server. First, switch to your OpManager directory:
cd /opt/ManageEngine/OpManager/binThen, start the Opmanager service on Debian 12 with the following command:
sudo ./StartOpManagerServer.sh
Wait until the process is completed. When it is completed, you should see:

This will provide you with a URL that you can use to access your OpManager dashboard from the web interface.
Step 4 – Access OpManager Monitoring Dashboard via Web Interface
At this point, you can follow the URL you have in your web browser to access the OpManager dashboard on Debian 12:
https://server-ip-address:8061You will see the OpManager login screen. Enter Admin as the default username and password. Click Login.
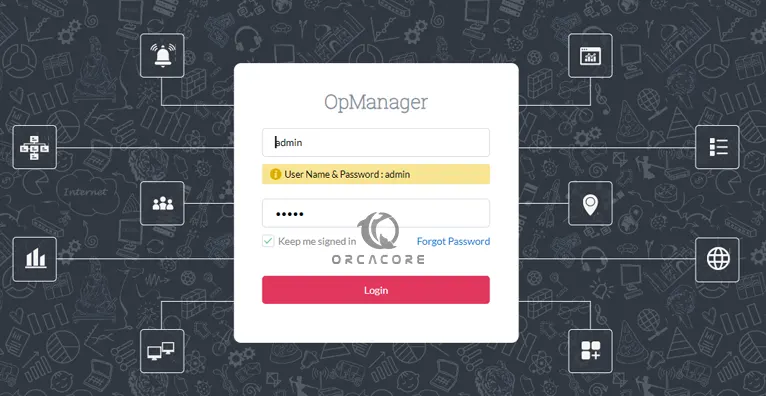
Then, you should see your OpManager Monitoring dashboard on Debian 12:
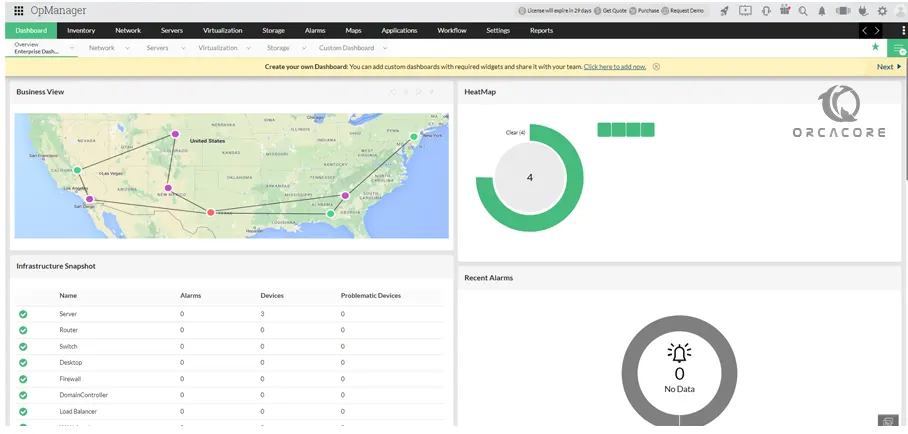
From the settings, you can simply change your admin password to increase your security. Then, you can easily add and monitor your desired servers and networks. After your trial version is finished you can purchase the enterprise version.
Step 5 – Manage OpManager as a Systemd Service
At this point, if you want to run your OpManager as a service, close the connection by pressing the ctrl + c in your terminal. Then, navigate to the OpManager bin directory:
cd /opt/ManageEngine/OpManager/binNow you can use the following command to run OpManager as a service:
sudo ./linkAsService.shExample Output:
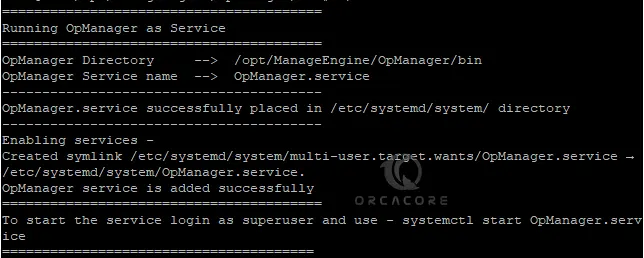
Then, start your OpManager service by using the command below:
sudo systemctl start OpManager.service
Verify your service is active and running:
sudo systemctl status OpManager.serviceExample Output:
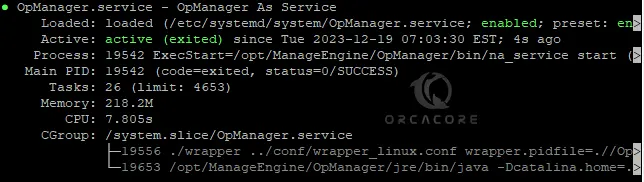
As you can see you can easily run your OpManager as a service on Debian 12.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned the Network Monitoring with OpManager Tool on Debian 12. You can easily get the installer from the ManageEngine official site and run your OpManager service. With OpManager, you can easily monitor your network devices and server.
Hope you enjoy using it. Also, you may like to read the following articles:



