Share your love
How To Set up PowerDNS on Ubuntu 22.04

In this guide, we intend to teach you How To Set up PowerDNS and PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04.
PowerDNS or pdns is an open-source (GPL) software. It provides software to create authoritative DNS, Recursive DNS, DNS loading balancer, Debugging tools, and APIs to provision zones and records. A complete suite of DNS-related software that you can use for your company.
Benefits of PowerDNS:
- Instant startup when hosting many domains
- Use of multi-core (32+ cores) processors
- Low memory requirement
- DNSSEC
- High performance
- Support different scripts
- Support different types of databases
- IPv6 support
Set up PowerDNS and PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04
To complete this guide, log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Ubuntu 22.04.
Install MariaDB on Ubuntu 22.04
In this guide, we use MariaDB as backend storage for PowerDNS zone files.
First, update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt updateThen, use the following command to install the required packages and dependencies:
sudo apt install software-properties-common gnupg2 curl git -yNow use the following command to install MariaDB on Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client -yStart and enable your MariaDB service:
# sudo systemctl start mariadb
# sudo systemctl enable mariadbCreate PowerDNS Database
At this point, you need to log in to your MariaDB shell by using the command below:
sudo mysql -u rootThen, from your MariaDB shell run the command below to create a PowerDNS database, here we named it powerdb:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE powerdb;Next, create a PowerDNS user and grant all the privileges to it. Here we named it poweruser, remember to choose a strong password for:
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON powerdb.* TO 'poweruser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';Finally, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB shell:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXITDisable systemd-resolved Service on Ubuntu 22.04
systemd-resolved is a system service that provides network name resolution to local applications. It implements a caching and validating DNS/DNSSEC stub resolver, as well as an LLMNR and MulticastDNS resolver and responder.
At this point, you need to disable and stop the systemd-resolved service by using the commands below:
# sudo systemctl stop systemd-resolved
# sudo systemctl disable systemd-resolvedThen, you need to remove the symbolic link for the /etc/resolv.conf file by using the command below:
# ls -lh /etc/resolv.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 102 Mar 16 08:10 /etc/resolv.conf
# sudo unlink /etc/resolv.confNext, use the following command to update the /etc/resolv.conf:
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" | sudo tee /etc/resolv.confSet up PowerDNS on Ubuntu 22.04
At this point, we will install PowerDNS from the APT repository.
To do this, you can use the command below:
sudo apt install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql -yWhen your installation is completed, you can configure your PowerDNS database.
Configure PowerDNS Database on Ubuntu 22.04
At this point, you need to import the PowerDNS database schema. To do this run the command below with the PowerDNS user and database that you have created before:
mysql -u poweruser -p powerdb < /usr/share/pdns-backend-mysql/schema/schema.mysql.sqlAfter the schema has been imported, you need to configure the PowerDNS connection details to the database. To do this, create and open a file with your favorite text editor, here we use the vi editor:
sudo vi /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/pdns.local.gmysql.conf Add the following lines to the file with your PowerDNS database values:
# MySQL Configuration
# Launch gmysql backend
launch+=gmysql
# gmysql parameters
gmysql-host=127.0.0.1
gmysql-port=3306
gmysql-dbname=powerdb
gmysql-user=poweruser
gmysql-password=password
gmysql-dnssec=yes
# gmysql-socket=When you are done, save and close the file.
Set the correct ownership and permission for the file:
# sudo chown pdns: /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/pdns.local.gmysql.conf
# sudo chmod 640 /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/pdns.local.gmysql.confNow you can verify your PowerDNS database connection on Ubuntu 22.04 by using the command below:
# sudo systemctl stop pdns.service
# sudo pdns_server --daemon=no --guardian=no --loglevel=9In your output you will see:
Output
...
Mar 16 08:25:49 Creating backend connection for TCP
Mar 16 08:25:49 gmysql Connection successful. Connected to database 'powerdb' on '127.0.0.1'.
Mar 16 08:25:49 About to create 3 backend threads for UDP
Mar 16 08:25:49 gmysql Connection successful. Connected to database 'powerdb' on '127.0.0.1'.
Mar 16 08:25:49 gmysql Connection successful. Connected to database 'powerdb' on '127.0.0.1'.
Mar 16 08:25:49 gmysql Connection successful. Connected to database 'powerdb' on '127.0.0.1'.
Mar 16 08:25:49 Done launching threads, ready to distribute questions
...Start and Enable PowerDNS Service
At this point, start and enable your PowerDNS service by using the following commands:
# sudo systemctl restart pdns
# sudo systemctl enable pdnsCheck PowerDNS Port
Verify that port 53 is open for PowerDNS on Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo ss -alnp4 | grep pdnsOutput
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pdns_server",pid=4402,fd=5))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pdns_server",pid=4402,fd=7))
You can also check if PowerDNS is responding to requests by using the command below:
dig @127.0.0.1Output
; <<>> DiG 9.18.1-1ubuntu1.1-Ubuntu <<>> @127.0.0.1
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: REFUSED, id: 19783
;; flags: qr rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;. IN NS
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) (UDP)
;; WHEN: Thu Mar 16 08:27:58 UTC 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 28
At this point, the installation of PowerDNS is completed, and you can proceed to the next step to install PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04.
Install PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04
With this Web-based admin tool, we can easily manage the PowerDNS server. To install PowerDNS admin, you need to install the Python development package and other required packages.
Install Required packages
First, use the following command to install the Python development package:
sudo apt install python3-dev -yThen, install the required build tools:
sudo apt install libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev libssl-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libxmlsec1-dev libffi-dev pkg-config apt-transport-https virtualenv python3-venv build-essential libmariadb-dev git python3-flask -yAt this point, you need to install Node.js on Ubuntu 22.04. To do this, use the following commands:
# curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_16.x | sudo -E bash -
# sudo apt install -y nodejsAlso, you need to have Yarn installed on your server. To do this, use the following commands to add the GPG key and repository and install Yarn:
# curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg >/dev/null
# echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg] https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list# sudo apt update
# sudo apt install yarn -yClone PowerDNS Admin Souce Code
At this point, you need to clone the PowerDNS admin source code on Ubuntu 22.04 by using the command below:
# sudo su -
# git clone https://github.com/ngoduykhanh/PowerDNS-Admin.git /var/www/html/pdnsCreate a Virtual Environment
At this point, you need to switch to your /var/www/html/pdns/ directory and create a virtual environment by using the commands below:
# cd /var/www/html/pdns/
# virtualenv -p python3 flaskActivate the environment and install the libraries specified in the requirements.txt:
# source ./flask/bin/activate
# pip install --upgrade pip
# pip install -r requirements.txtAfter that, use the following command to deactivate your environment:
deactivateNow you need to configure the PowerDNS admin connectivity to your database.
Configure PowerDNS Admin Connection to PowerDNS Database
To do this, you need to edit the following file:
vi /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin/default_config.pyFind the lines below and change them to your PowerDNS database details:
### DATABASE CONFIG
SQLA_DB_USER = 'poweruser'
SQLA_DB_PASSWORD = 'password'
SQLA_DB_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SQLA_DB_NAME = 'powerdb'
SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = True
....When you are done, save and close the file.
Create a Database Schema
To do this, you can run the following commands step by step:
# cd /var/www/html/pdns/
# source ./flask/bin/activate
# export FLASK_APP=powerdnsadmin/__init__.py
# flask db upgradeWhen you are finished, you should get an output similar to this:
Output
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade -> 787bdba9e147, Init DB
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 787bdba9e147 -> 59729e468045, Add view column to setting table
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 59729e468045 -> 1274ed462010, Change setting.value data type
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 1274ed462010 -> 4a666113c7bb, Adding Operator Role
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 4a666113c7bb -> 31a4ed468b18, Remove all setting in the DB
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 31a4ed468b18 -> 654298797277, Upgrade DB Schema
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 654298797277 -> 0fb6d23a4863, Remove user avatar
...Next, you need to generate the asset files using Yarn on Ubuntu 22.04:
# yarn install --pure-lockfile
# flask assets buildLast, deactivate your virtual environment:
deactivateEnable PowerDNS API access on Ubuntu 22.04
At this point, you need to edit the following file to enable PowerDNS API access:
sudo vi /etc/powerdns/pdns.confFind the sections below and add the following lines shown below:
# api Enable/disable the REST API (including HTTP listener)
#
# api=no
api=yes
#################################
# api-key Static pre-shared authentication key for access to the REST API
#
# api-key=
api-key=2315d9cd-047e-4dc2-8fde-3efa9092aeed #You can generate one from https://codepen.io/corenominal/pen/rxOmMJWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Finally, restart PowerDNS on Ubuntu 22.04 to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart pdnsCreate PowerDNS Admin Virtual Host File on Ubuntu 22.04
To complete this step, you need to install Nginx on your server:
sudo apt install nginx -yThen, use the following command to create and open a PowerDNS virtual host file:
sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/powerdns-admin.confAdd the following content to the file:
server {
listen *:80;
server_name your-domain-name;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /var/www/html/pdns;
access_log /var/log/nginx/pdnsadmin_access.log combined;
error_log /var/log/nginx/pdnsadmin_error.log;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffers 32 4k;
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 64;
location ~ ^/static/ {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
root /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin;
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {
expires 365d;
}
location ~* ^.+.(css|js)$ {
expires 7d;
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
proxy_connect_timeout 120;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}When you are done, save and close the file.
Rename the default Nginx file with the command below:
sudo mv /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default{,.old}Check the syntax of your created file:
nginx -tOutput
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulNext, set the correct ownership for the file:
sudo chown -R www-data: /var/www/html/pdnsRestart Nginx to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart nginxManage PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04
To start and enable your service, you need to create a system unit file for PowerDNS Admin.
create and open the file with the following command:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.serviceAdd the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin
Requires=pdnsadmin.socket
After=network.target
[Service]
PIDFile=/run/pdnsadmin/pid
User=pdns
Group=pdns
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/html/pdns
ExecStart=/var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/pdnsadmin/pid --bind unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket 'powerdnsadmin:create_app()'
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetWhen you are done, save and close the file.
Also, you need to create a socket file for PowerDNS Admin:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.socketAdd the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin socket
[Socket]
ListenStream=/run/pdnsadmin/socket
[Install]
WantedBy=sockets.targetwhen you are done, save and close the file.
Next, create an environment file:
# mkdir /run/pdnsadmin/
# echo "d /run/pdnsadmin 0755 pdns pdns -" >> /etc/tmpfiles.d/pdnsadmin.confSet the correct permissions for it:
# chown -R pdns: /run/pdnsadmin/
# chown -R pdns: /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin/Finally, reload the system daemon:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadNext, use the following commands to start and enable the PowerDNS Admin service on Ubuntu 22.04:
sudo systemctl enable --now pdnsadmin.service pdnsadmin.socketVerify your PowerDNS Admin is active and running on your server:
#sudo systemctl status pdnsadmin.service
● pdnsadmin.service - PowerDNS-Admin
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.service; enabled; vendor pre>
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-03-16 08:45:32 UTC; 17s ago
TriggeredBy: ● pdnsadmin.socket
Main PID: 9831 (gunicorn)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4575)
...
#sudo systemctl status pdnsadmin.socket
● pdnsadmin.socket - PowerDNS-Admin socket
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.socket; enabled; vendor pres>
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-03-16 08:45:32 UTC; 58s ago
Triggers: ● pdnsadmin.service
Listen: /run/pdnsadmin/socket (Stream)
CGroup: /system.slice/pdnsadmin.socket
...Access PowerDNS Admin Web Interface
At this point, you can access your PowerDNS Admin web interface by typing your server’s IP or Domain name in your web browser:
http://domain_name
or
http://IP_addressBegin by creating the admin user account. With the required details provides, click register to create the account.
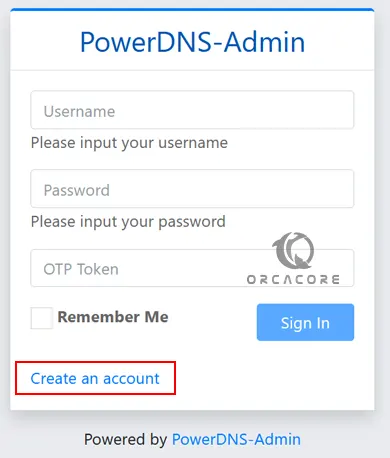
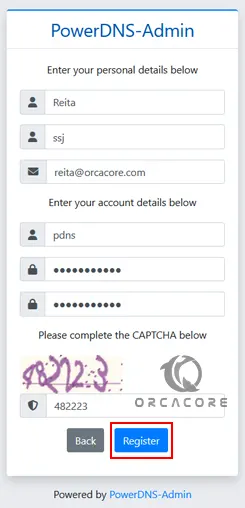
Now login to the PowerDNS Admin interface using the created user credentials.
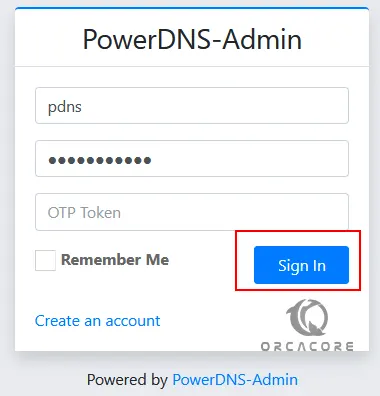
Next, you should provide the PowerDNS API URL to connect to PowerDNS and manage it. Then, click on the Save Settings button to save the changes.

Click on the Dashboard button. You should see the PowerDNS admin dashboard. There are many configurations you can make to your server using the PowerDNS admin web UI such as editing the domain templates, removing domains, managing user accounts, etc. You can view the history of activities performed as well.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Set up PowerDNS and PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 22.04.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these articles:
How To Set up Gradle on Ubuntu 22.04



