Share your love
Enable TCP BBR on Centos 7 – Increase Network Speed

This guide intends to teach you to Enable TCP BBR on Centos 7. It stands for TCP Bottleneck Bandwidth and Round-trip propagation time. TCP BBR is a congestion control algorithm developed by Google. Also, it provides better network performance by managing congestion and optimizing throughput, resulting in improved user experience and faster data transfers. Now you can follow the steps below to increase your Network speed by enabling TCP BBR on Centos 7.
Steps To Enable TCP BBR on Centos 7 To Help the Boosting Network Speed
Before you start to Enable TCP BBR on Centos 7, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. For this purpose, you can check the Centos 7 Initial Setup Guide.
Then, follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Step 1 – Check the Current Congestion Algorithm on Centos 7
First, you need to update your local packages with the command below:
sudo yum update -yThen, run the following command to Check the Current Congestion Algorithm on Centos 7:
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_controlMost of the Linux distros use Cubic and Reno algorithms. In your output, you should see something similar to this:
Output
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = cubicAlso, you can use the commands below to check the available Congestion Algorithms on Centos 7:
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_controlOutput
net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control = cubic renoAs you can see, Cubic and Reno are available as the congestion algorithms. To add the TCP BBR, you can follow the steps below.
Step 2 – Install New Kernel on Centos 7
If you don’t install the new kernel, during the adding TCP BBR on Centos 7, you will get the following error:
Error
sysctl: setting key "net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control": No such file or directory
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbrSo you must use the following commands to install the Elrepo and get the latest kernel:
# sudo rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
# sudo rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-3.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
# sudo yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-mlThen, edit file /etc/default/grub. Search for the line containing GRUB_DEFAULT and set it to 0.
GRUB_DEFAULT=0Save and close the file.
Next, you need to create a new grub configuration file and reboot your Centos 7 to apply the changes:
# sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
# sudo rebootStep 3 – Add BBR As the Default Congestion Algorithm on Centos 7
At this point, you can add and enable TCP BBR as your default congestion algorithm. To do this, you need to open the sysctl.conf file with your desired text editor like Vi Editor or Nano Editor:
sudo vi /etc/sysctl.confAdd the following content to the file to Enable TCP BBR on Centos 7:
net.core.default_qdisc=fq
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=bbrYour file should look like this:
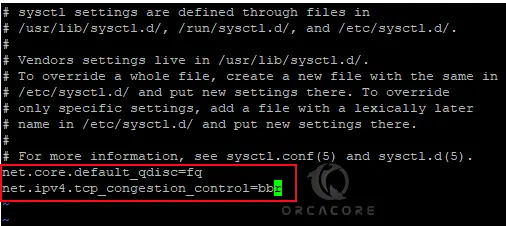
When you are done, save and close the file.
Then, reload the configuration file with the command below:
sudo sysctl -pOutput
net.core.default_qdisc = fq
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbrStep 4 – Verify TCP BBR is Enabled and Activated on Centos 7
At this point, you need to verify that BBR is enabled and active as the new TCP congestion control by using the following command on Centos 7:
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_controlOutput
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbrAlso, you can use the command below to verify it:
lsmod | grep bbrOutput
tcp_bbr 16384 5Finally, list available TCP congestion controls on your server again:
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_controlYou should see BBR in your list:
Output
net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control = reno cubic bbrThat’s it. You have successfully added BBR to your Centos 7.
Conclusion
By following the guide steps, you can enable TCP BBR on CentOS 7, setting it as the default congestion algorithm, improving network performance, and optimizing throughput. Hope enjoy it. Also, you may like to read the following articles:



