Share your love
Open and Close Ports with FirewallD on Rocky Linux 8

In this guide from the Orcacore website, we want to teach you how to open and close ports with FirewallD on Rocky Linux 8. FirewallD is a tool that acts as a firewall in Linux operating systems. It helps protect the system from unusual traffic and secures different protocols by disabling their defaults. Opening a port allows specific types of network traffic (like HTTP on port 80 or SSH on port 22) to reach the server, while closing a port blocks unwanted access.
Table of Contents
Steps To Open and Close Ports with FirewallD on Rocky Linux 8
To complete this guide, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide on the Initial Server Setup with Rocky Linux 8.
1. Check FirewallD Status on Rocky Linux 8
The first step is to check whether you have the FirewallD service active on your server or not. To do this, run the command below:
sudo systemctl status firewalldIn my case, I get the following output:
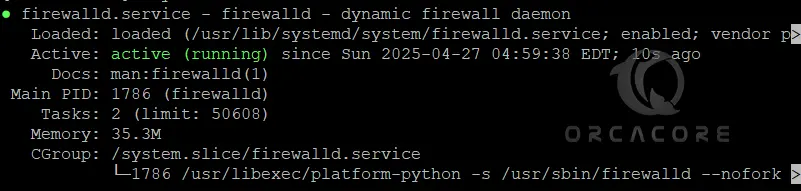
If FirewallD is not running, use the following commands to start and enable it:
# sudo systemctl start firewalld
# sudo systemctl enable firewalldIf your service is not available, you can install FirewallD with the following command:
# sudo dnf update -y
# sudo dnf install firewalld -y2. List Open Ports and Services With FirewallD
At this point, you need to confirm that any particular port is not already active in firewalld and has not been allowed to access through public connections on Rocky Linux 8. To do this, run the following command:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all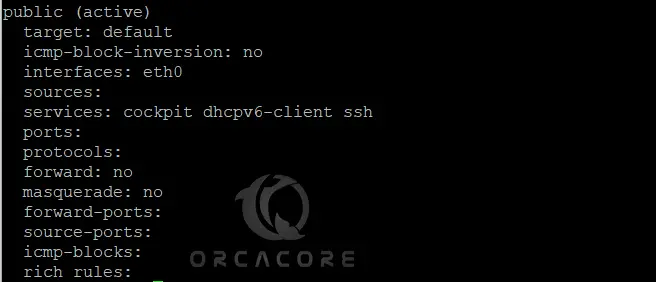
Also, FirewallD comes with some pre-configured services, for which and their ports the firewall allows public communication by default. And SSH, Plex, Cockpit, etc, are a few of them. You can check the list of all such services by using the command below:
sudo firewall-cmd --get-services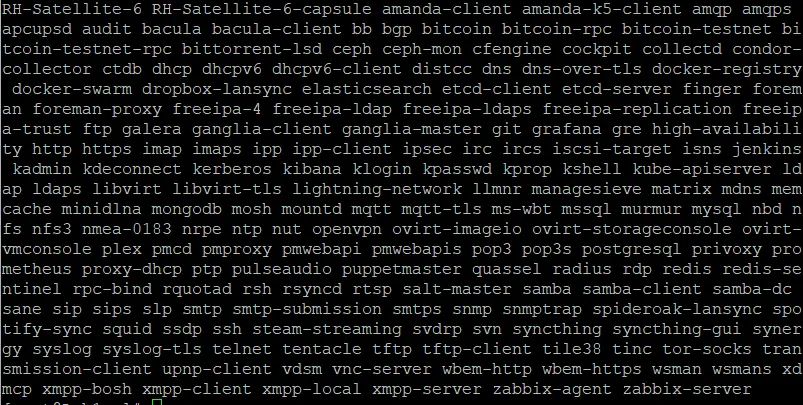
These are the services that are available on firewalld as pre-configured and can be opened just using their names.
List Zones with FirewallD
At this point, you can access any service that you have just allowed the service in the public zone; however, just for information, you can check other available zones as well, in case you want to use any of them.
sudo firewall-cmd --get-zonesOutput
block dmz drop external home internal nm-shared public trusted work3. How to Open a Port or Service on Rocky Linux 8?
You can simply open a port or a service from the Public zone, with the following commands:
To open a Service, run:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=service-nameFor example, opening HTTP traffic through the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=httpTo open a Particular Port, run:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port type-port-number/tcpFor example, open port 1000:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port 1000/tcpNote: After any changes, remember to reload FirewallD to apply the changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload4. How to Close a Port or Service on Rocky Linux 8?
You can simply use the FirewallD commands to block a port or service.
To block a Service, run:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --remove-service service-nameTo block a particular port, run:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --remove-port type-numberRemember to reload FirewallD after your changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadFor more information, you can visit the FirewallD Documentation page.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned Open and Close Ports with FirewallD on Rocky Linux 8. Managing open and closed ports with FirewallD on Rocky Linux 8 is an essential step in securing your server. By allowing only necessary traffic, you reduce the risk of attacks and unauthorized access.
Hope you enjoy it. You may also like these articles:
Install and Configure Redis on Rocky Linux 8
Introducing AlmaLinux As a Replacement for CentOS
Enable FirewallD GUI on Rocky Linux 8
FirewallD Configuration on AlmaLinux 9
FAQs
How do I permanently open a port with FirewallD?
You can use this command: firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=PORT/protocol
What’s the difference between temporary and permanent rules in FirewallD?
Temporary rules are lost after a reboot, while permanent rules stay active across reboots.
Can I open a port for a specific zone only in FirewallD?
Yes, by specifying the zone with --zone=ZONE in your command, you can open the port. For example: firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=PORT/protocol



