Share your love
GlassFish Setup with Nginx Reverse Proxy on Debian 13

In this guide, you will learn comprehensive steps for GlassFish Setup with Nginx Reverse Proxy on Debian 13. GlassFish is an open-source application server used to run and deploy Java-based web applications and services. It supports Java EE (now Jakarta EE) specifications and is commonly used for hosting enterprise-scale web apps, REST APIs, and microservices.
You can now proceed to the guide steps below on the Orcacore website to complete GlassFish Setup with Nginx Reverse Proxy on Debian 13.
Table of Contents
GlassFish Setup with Nginx Reverse Proxy on Debian 13
Before you start the guide steps, be sure to have access to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. Also, you need a domain name that points to your server’s IP address.
1. Installing Java For GlassFish
First, you must run the system update and upgrade with the following commands:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThen, install OpenJDK by using the following command:
sudo apt install default-jdk -yVerify Java installation by checking its version:
java --version
2. Set up GlassFish on Debian 13
At this point, you must download the latest GlassFish package from the official downloads page by using the following command:
# cd /opt
# sudo wget https://download.eclipse.org/ee4j/glassfish/glassfish-7.0.24.zipExtract your downloaded file with the following command:
sudo unzip glassfish-7.0.24.zipCreate GlassFish Systemd Unit File
To manage your GlassFish server as a service, you need to create a systemd unit file. Use your desired text editor, like Vi Editor or Nano Editor, to create the file:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/glassfish.serviceAdd the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description = GlassFish Server v7.0
After = syslog.target network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/opt/glassfish7/bin/asadmin start-domain
ExecReload=/opt/glassfish7/bin/asadmin restart-domain
ExecStop=/opt/glassfish7/bin/asadmin stop-domain
Type = forking
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.targetNote: Remember to replace the correct path of your GlassFish server installation. Once you are done, save and close the file.
Start and Enable GlassFish Service
Then, reload the system service, start, and enable your GlassFish service on Debian 3 by running the commands below:
# sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# sudo systemctl start glassfish
# sudo systemctl enable glassfishVerify GlassFish is active and running:
sudo systemctl status glassfish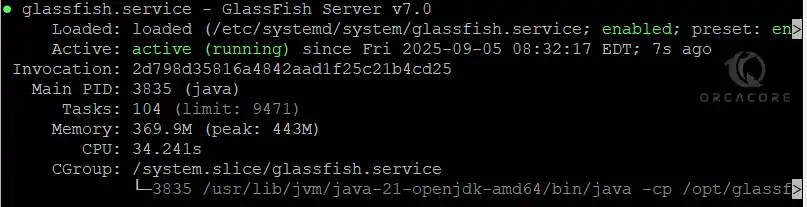
Set GlassFish Admin User Password
The default GlassFish admin password is blank. So, you must set a password for your GlassFish admin user.
GlassFish has a tool called asadmin that accepts commands for setting up GlassFish via a command line. To use this command-line utility, you must make it executable with the command below:
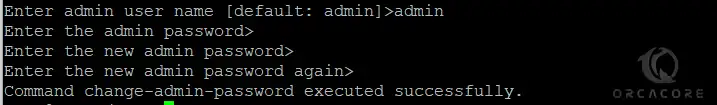
sudo export PATH=/opt/glassfish7/bin:$PATHThen, run the following command to set an admin password for GlassFish:
sudo asadmin --port 4848 change-admin-passwordYou will be asked to enter the admin password, press enter to set a new password:
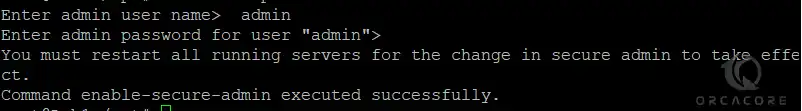
Now you can enable the secure admin feature for GlassFish:
sudo asadmin --port 4848 enable-secure-adminEnter the admin user and password to complete it:
Restart GlassFish to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart glassfishSet up Firewall Rules for GlassFish
At this point, we assumed that you have a running FW firewall. Now you must allow the following ports through your firewall so that you can access your GlassFish dashboard via the web interface:
# sudo ufw allow 4848/tcp
# sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp
# sudo ufw allow 80/tcpApply the new rules by reloading the firewall:
sudo ufw reload3. Access GlassFish Admin Console on Debian 13
At this point, you can access the default GlassFish page by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser, followed by 8080:
http://your-server-IP:8080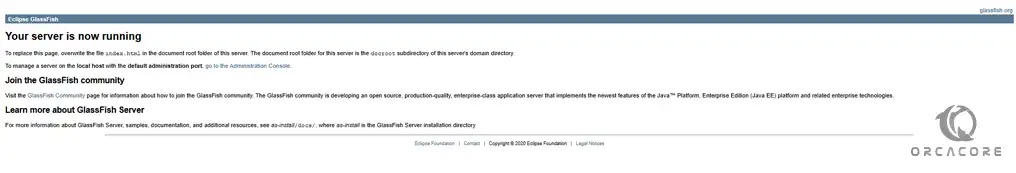
Also, you can access the web administrator console by typing your Server’s IP address in your web browser, followed by 4848:
http://your-server-IP:4848You will see the GlassFish Administration console login screen. Enter your Admin user and password you have configured and press Login.
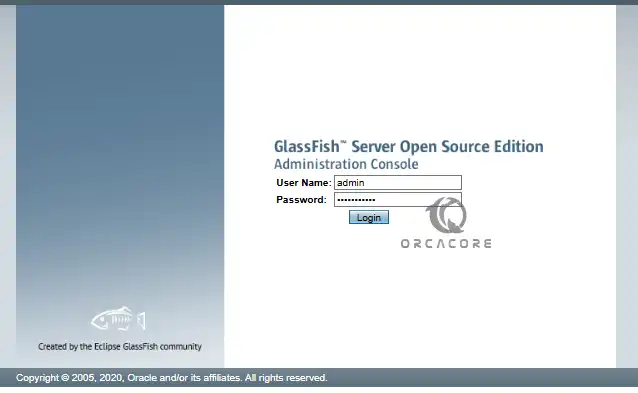
You will have the GlassFish admin console:
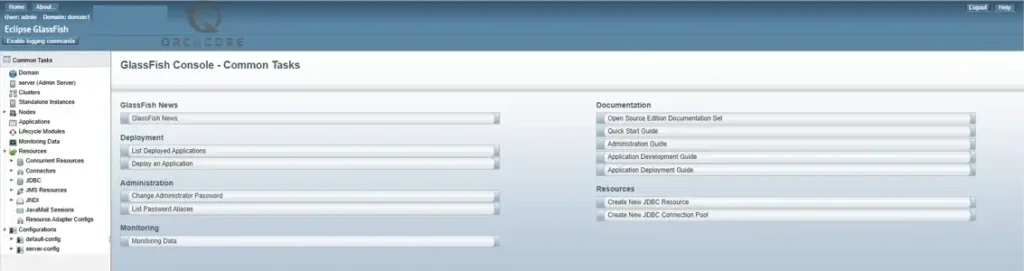
4. Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Glassfish
Now you can use Nginx reverse proxy to access the GlashFish admin console. With this option, you can access your application without using port 8080.
First, install Nginx on Debian 13:
sudo apt install nginx -yThen, create an Nginx virtual host configuration file with the following command:
sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/glassfish.confAdd the following configuration to the file:
upstream glassfish {
server server-ip:8080 weight=100 max_fails=5 fail_timeout=5;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://glassfish;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Once you are done, save and close the file.
Confirm Nginx for any syntax errors using the following command:
sudo nginx -t
Restart Nginx to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart nginxAlso, you can check for Nginx status:
sudo systemctl status nginx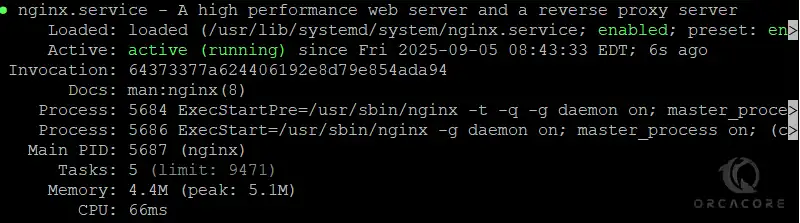
You can now access the Glassfish admin console using the URL http://your-domain:4848.
Conclusion
At this point, you have completed GlassFish Setup with Nginx Reverse Proxy on Debian 13. You can now start deploying your Java-based application on the Glassfish server. Hope you enjoy it. Please subscribe to us on Facebook, X, and YouTube.
You may also like to read the following articles:
ConfigServer Is Closed on 31 August 2025
Synchronize System Time with NTP in Debian 13



