Share your love
Install bmon Real-Time Bandwidth Monitor on AlmaLinux 9

This tutorial intends to teach you to Install and Use bmon Real-Time Network Bandwidth Monitor on AlmaLinux 9. bmon is a free and open-source monitoring and debugging command-line tool. It is used to monitor and display network bandwidth usage on a system.
You can follow this guide to start your bmon installation in the latest version on AlmaLinux 9 and start using it.
Steps To Install and Use bmon Real-Time Network Bandwidth Monitor on AlmaLinux 9
To set up bmon, you must have access to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow this guide on Initial Server Setup with AlmaLinux 9.
Now follow the steps below to complete this guide.
Step 1 – Build and Install bmon from Source on AlmaLinux 9
First, you must run the system update with the following command:
sudo dnf update -yAlso, install the Epel repository with the command below:
sudo dnf install epel-release -yThen, install the required packages for bmon on your AlmaLinux server by using the command below:
sudo dnf install make libconfuse-devel libnl3-devel ncurses-devel git autoconf automake gcc -yNext, clone the bmon from the source by using the command below on AlmaLinux 9:
sudo git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.gitOutput
Cloning into 'bmon'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 706, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 706 (delta 0), reused 1 (delta 0), pack-reused 703
Receiving objects: 100% (706/706), 860.74 KiB | 3.77 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (395/395), done.
When your download is completed, switch to your bmon directory with the command below:
cd bmonNow run the following commands to build and install the bmon Real-Time Bandwidth Monitor tool:
# sudo ./autogen.sh
# sudo ./configure
# sudo make
# sudo make installStep 2 – Run bmon to Check Real-Time Bandwidth Usage on AlmaLinux 9
After your installation is completed, you can run your bmon service to monitor live bandwidth usage on your server:
bmonOn your screen, you will see something similar to this:
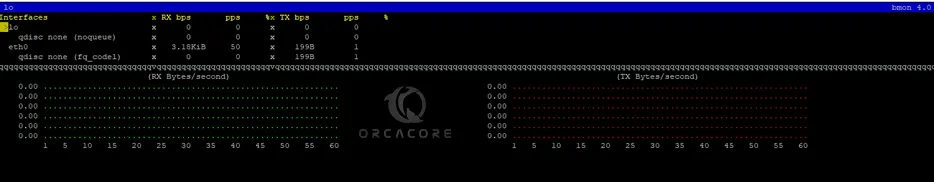
Step 3 – How To Use bmon Bandwidth Monitoring Tool?
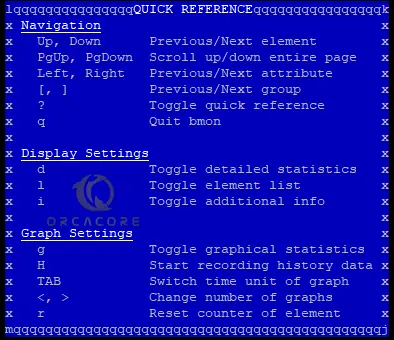
To get a quick reference of bmon, you can press Shift + ? in your terminal. You will see:
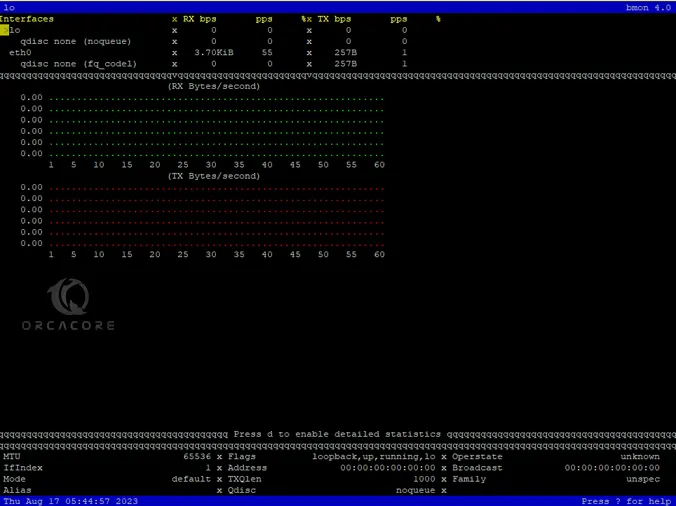
By default, bmon only shows interface information. To load the graphics you can press g, i, or d for detailed graphical visualization of information.
Also, you can use bmon to monitor a specific bandwidth network interface on AlmaLinux 9. To do this, you can use the -p option with your desired interface. For example:
bmon -p eth0To get the results in bit per second, you can use the -b flag. For example:
bmon -bp eth0You can define the intervals per second by using the -r option. For example:
bmon -r 2 -p eth0Step 3.1 – Use bmon Input Modules
Netlink is used to transfer information between the kernel and user-space processes. By default, Netlink is the input module. To use bmon Netlink input modules, you can use the following command on AlmaLinux 9:
bmon -i netlink 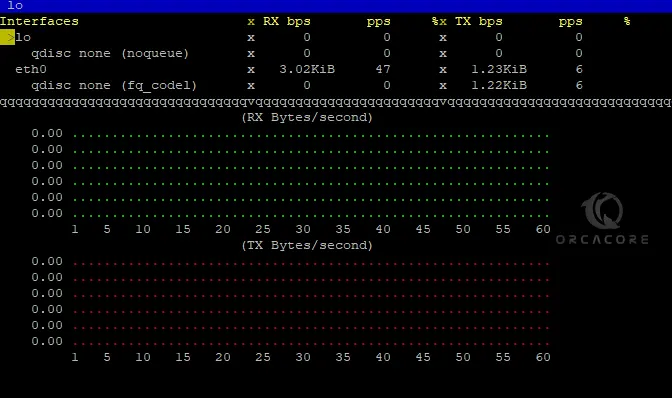
Also, you can use proc as an input module. To do this, you can run the command below:
bmon -i proc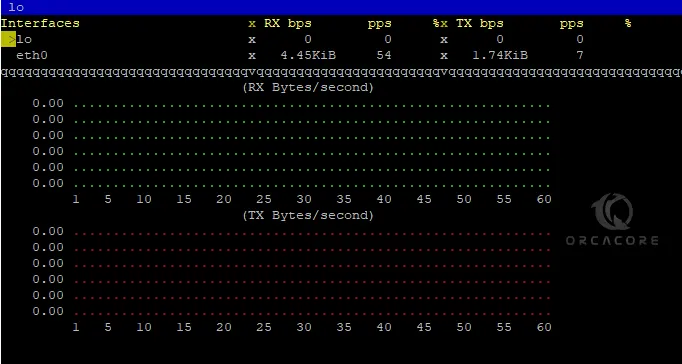
dummy is the programmable input module for debugging & testing purposes. You can use dummy as an input module for bmon:
bmon -i dummy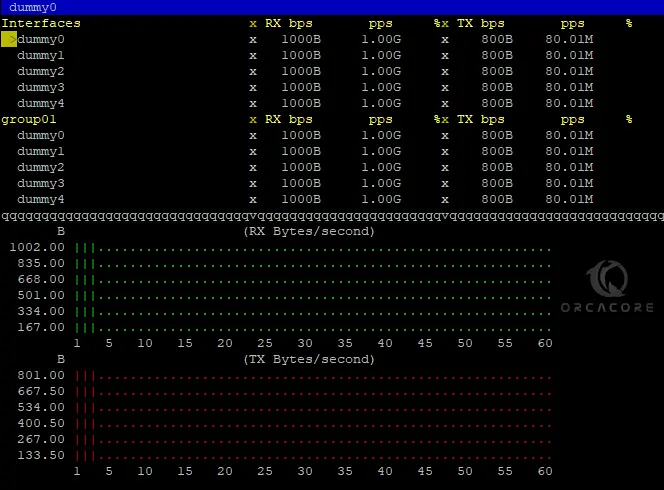
To disable the data collection, you can use Null with your bmon on AlmaLinux 9:
bmon -i nullStep 3.2 – Use bmon Output Modules
curses are used as a display library for text-based terminals. By default, curses are the output modules. To get output in curses, run the following bmon command:
bmon -o curses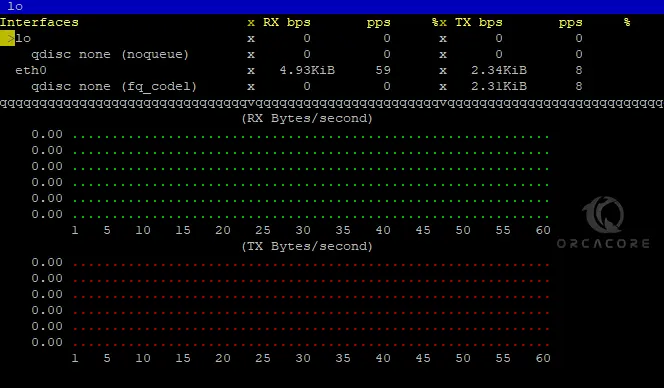
When curses are not available, you can use ascii instead. To get output in ascii, run the following bmon command on AlmaLinux 9:
bmon -o ascii Output
Interfaces RX bps pps % TX bps pps %
lo 0 0 0 0
qdisc none (noqueue) 0 0 0 0
eth0 0 0 0 0
qdisc none (fq_codel) 0 0 0 0
Interfaces RX bps pps % TX bps pps %
lo 0 0 0 0
qdisc none (noqueue) 0 0 0 0
eth0 3.49KiB 54 1.41KiB 3
qdisc none (fq_codel) 0 0 1.41KiB 3
Interfaces RX bps pps % TX bps pps %
lo 0 0 0 0
qdisc none (noqueue) 0 0 0 0
eth0 3.23KiB 51 930B 2
qdisc none (fq_codel) 0 0 930B 2
Interfaces RX bps pps % TX bps pps %
lo 0 0 0 0
...Also, you can use format mode to get the output. To do this, you can run the command below:
bmon -o formatOutput
lo 864 864 6 6
qdisc none (noqueue) unknown unknown unknown unknown
eth0 772373799 7184990 718996 63774
qdisc none (fq_codel) unknown unknown unknown unknown
lo 864 864 6 6
qdisc none (noqueue) unknown unknown unknown unknown
eth0 772376874 7186270 719042 63776
qdisc none (fq_codel) unknown unknown unknown unknown
lo 864 864 6 6
qdisc none (noqueue) unknown unknown unknown unknown
eth0 772379971 7186548 719091 63777
qdisc none (fq_codel) unknown unknown unknown unknown
lo 864 864 6 6
qdisc none (noqueue) unknown unknown unknown unknown
eth0 772383396 7186946 719145 63780
qdisc none (fq_codel) unknown unknown unknown unknown
lo 864 864 6 6
...To get more help and information, you can use the following commands:
# bmon --help
# man bmon Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Build and Install the bmon Real-Time Network Bandwidth Monitor Tool on AlmaLinux 9, Run the service, and start using it with input and output modules. Hope you enjoy using it.
You may be interested in these articles:
Install Nagios Monitoring Tool on AlmaLinux 9



