Share your love
Install and Configure Jenkins on Debian 11

This tutorial intends to teach you to Install and Configure Jenkins on Debian 11.
Introduction to Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source continuous integration/continuous delivery and deployment (CI/CD) automation DevOps tool written in Java. It is used to implement CI/CD workflows, called pipelines.
Pipelines automate testing and reporting on isolated changes in a more extensive code base in real time and facilitate the integration of disparate branches of the code into a main branch. They also rapidly detect defects in a code base, build the software, automate testing of their builds, prepare the code base for deployment (delivery), and ultimately deploy code to containers and virtual machines, as well as bare metal and cloud servers.
Steps To Install and Configure Jenkins on Debian 11
To complete this guide, log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide on Initial Server Setup with Debian 11.
Install OpenJDK on Debian 11
Because Jenkins is written in Java, you must have installed it on your server. First, update your local package index with the following command:
sudo apt updateThen, use the following command to install OpenJDK:
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk -yVerify your Java installation by checking its version:
java -versionOutput
openjdk version "11.0.18" 2023-01-17
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.18+10-post-Debian-1deb11u1)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.18+10-post-Debian-1deb11u1, mixed mode, sharing)
Set up Jenkins on Debian 11
At this point, you need to add the Jenkins GPG key and Enable its repository. To do this, follow the steps below.
Add Jenkins GPG key
Jenkins packages aren’t available in the default Debian 11 repository. So you need to add it manually to your server.
First, install curl on Debian 11:
sudo apt install curl -yThen, add the Jenkins GPG key by using the following curl command:
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \
/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/nullAdd Jenkins Repository
Now you need to add the Jenkins repo to your Debian server by using the following command:
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/nullRun System Update
At this point, run the system update by using the command below:
sudo apt updateJenkins Installation on Debian 11
Finally, use the following command to install Jenkins on Debian 11:
sudo apt install jenkins -yJenkins Service Status
When your installation is completed, your Jenkis service must be started on your Debian 11 automatically. To confirm it, run the command below:
sudo systemctl status jenkinsOutput
● jenkins.service - Jenkins Continuous Integration Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/jenkins.service; enabled; vendor prese>
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-04-13 06:08:52 EDT; 1min 24s ago
Main PID: 5222 (java)
Tasks: 43 (limit: 4679)
Memory: 1.2G
CPU: 1min 9.528s
CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
└─5222 /usr/bin/java -Djava.awt.headless=true -jar /usr/share/java>If the service is not running or active, you can use the following command:
sudo systemctl enable --now jenkinsJenkins Administrator password
To access the Jenkins dashboard, you need your Jenkins admin password. By default, Jenkins’s password is available in the /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/. To find it, you can use the following command:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordOutput
91d9db64647b4260b457fa1c17765159
Configure Jenkins through Web Interface
At this point, you can access your Jenkins web interface by typing your server’s IP address in your web browser followed by 8080:
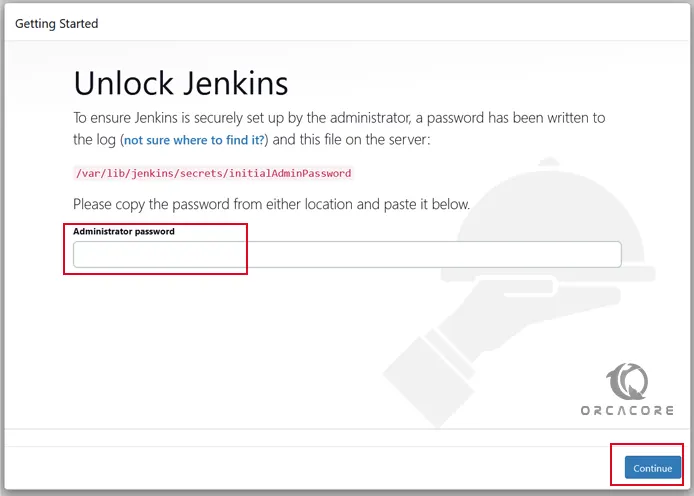
http://your-server-ip:8080You will see the Unlock Jenkins page. Enter your Jenkins initial admin password and click Continue.
Next, you should choose which Jenkins plugins you want to install on Debian 11. You can select plugins or the recommended ones. Here we choose Install suggested plugins.

This will take some time to complete.
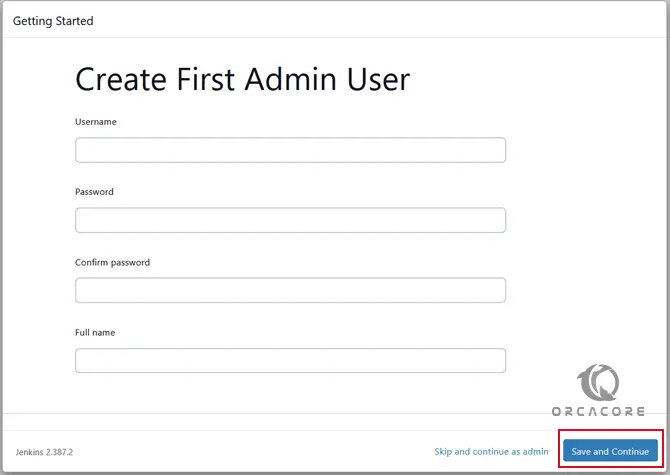
Then, you can create your first admin user. You can use this to log in and use Jenkins in the future.
Access Jenkins Dashboard on Debian 11
Finally, after following the other few steps you will have your Dashboard to start creating projects for testing and developing along with your developer’s Team.
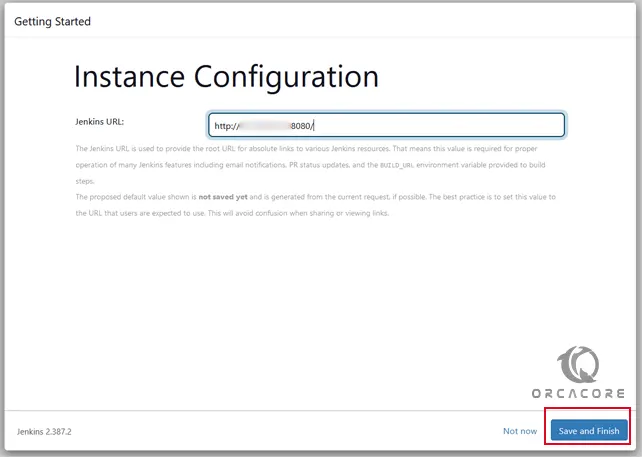
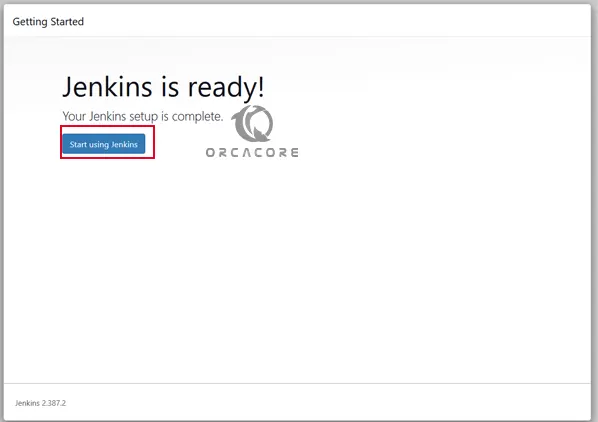
You should see your Jenkins dashboard:
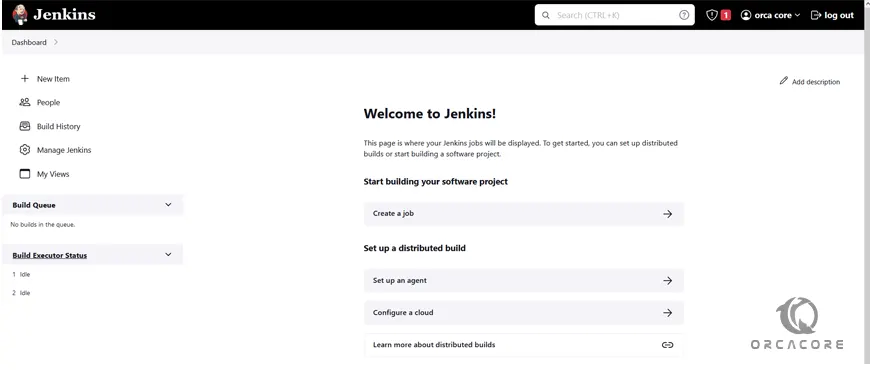
For more information, you can visit the Jenkins Docs page.
Conclusion
At this point, you have learned to Install and Configure Jenkins on Debian 11.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be interested in these articles:
Install OTRS Community Edition on Debian 11



