Share your love
How To Install Tor Browser on CentOS 7

In this guide, you will learn How To Install Tor Browser on CentOS 7. The Tor (the onion routing) browser is a web browser designed for anonymous web surfing and protection against traffic analysis. Although Tor is often associated with the darknet and criminal activity, law enforcement officials, reporters, activists, whistleblowers, and ordinary security-conscious individuals often use the browser for legitimate reasons.
The Tor browser works by using a technology known as onion routing. The onion router is a peer-to-peer (P2P) overlay network that enables users to browse the internet anonymously. Onion routing uses multiple layers of encryption to conceal both the source and destination of information sent over the network. It is designed so that no one can monitor or censor online communication.
Once a user installs Tor, the browser uses Tor servers to send data to an exit node, which is the point at which data leaves the network. Once this data has been sent, it is encrypted multiple times before being sent to the next node. Repeating this process makes it difficult to trace the data back to the source. In addition to encryption, the Tor browser does not track browsing history or store cookies.
You can now proceed to the guide steps below on the Orcacore website to set up Tor Browser on CentOS 7.
Table of Contents
Steps To Install Tor Web Browser on CentOS 7
To complete this guide on install Tor browser, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges. To do this, you can follow our guide on the Initial Server Setup with CentOS 7.
1. Create a Yum Repository For Tor Web Browser
The Tor development team provides an official yum repository for the Tor browser installation. You can find the latest available packages by visiting rpm.torproject.org.
First, you need to install the EPEL repository on CentOS 7:
sudo yum install epel-release -yNow, create a new file /etc/yum.repos.d/tor.repo with your favorite text editor, here we use vi:
sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/tor-browser.repo Add the following content to the file:
[Tor]
name=Tor for Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch
baseurl=https://rpm.torproject.org/centos/$releasever/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://rpm.torproject.org/centos/public_gpg.key
cost=100When you are done, save and close the file.
Then, update your local package index with the command below:
sudo yum update -y2. Install Tor Browser on CentOS 7
At this point, you have successfully added the Tor browser repository to your system. Next, use the yum command to install Tor Browser on your CentOS 7:
sudo yum install tor -yWhen your installation is completed, you can verify your Tor installation by checking its version:
tor --versionIn your output, you will see:
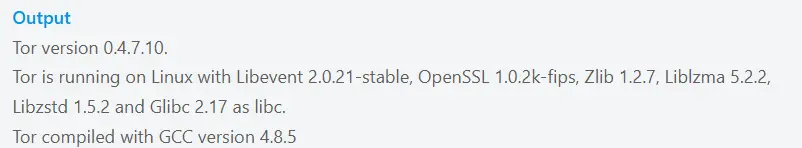
Important Note: It is highly recommended to use the Tor browser bundle, but if you want to use Firefox with Tor, once you have started the service, open firefox settings >> Preferences >> advanced >> network >> settings and select manual proxy configuration.
On successful command execution, you will have installed the Tor browser on your server. Now you can launch the application on your Desktop system.
Conclusion
Installing the Tor Browser on CentOS 7 is a simple process that enhances your online privacy and security. Though CentOS 7 is a bit dated, the Tor Browser remains compatible and offers a secure browsing experience right out of the box.
Hope you enjoy it. You may be like these guides:
Secure MySQL Connections with SSL on CentOS 7



